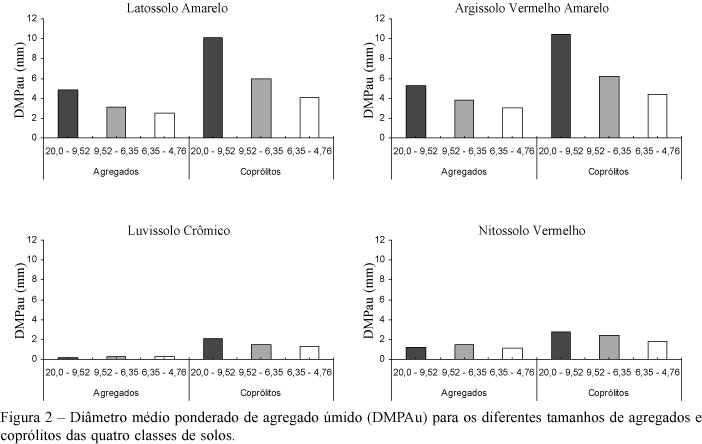
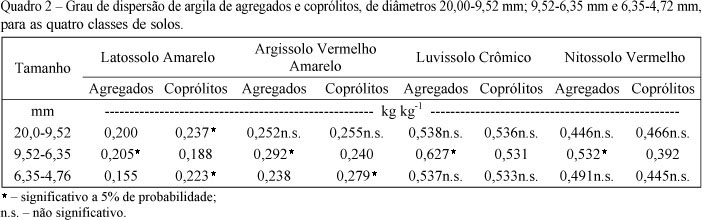
The soil structure is composed by pedogenic and biogenic aggregates, formed respectively by aggregate hierarchy and macrofauna activity, especially by earthworms. The objective of this study was to compare soil aggregates and earthworm casts with different aggregate-size classes and soil classes. The sampling of undisturbed soil and earthworm casts (Pontoscolex corethrurus, Muller, 1857) was made in four soils of different classes in the State of Paraíba (Oxisol, Ultisol, Alfisol and Nitisol). The chemical and physical evaluations of aggregates and earthworm casts were determined after dry and split into three aggregate-size classes (20.0 to 9.52, 9.52 to 6.35 and 6.35 to 4.76 mm). The particle-size distribution was similar to aggregates and earthworm casts, independent of aggregate-size classes. Earthworm casts had higher proportions of clay, silt and fine sand, lower coarse sand, higher physical stability and more organic carbon and cations contents than the pedogenic aggregates. These results show a peculiar genetic process that makes biogenic aggregates an important indicator of soil quality.
Macrofauna; aggregate stability; biologic activity; soil quality