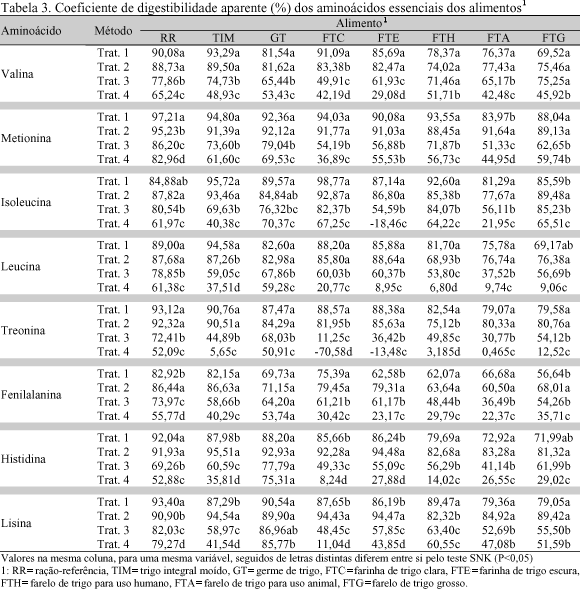
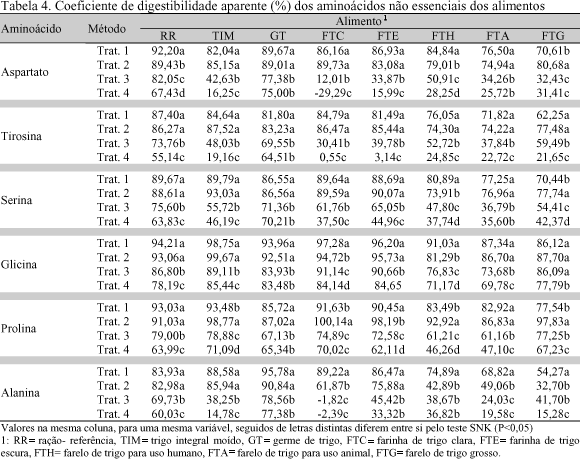
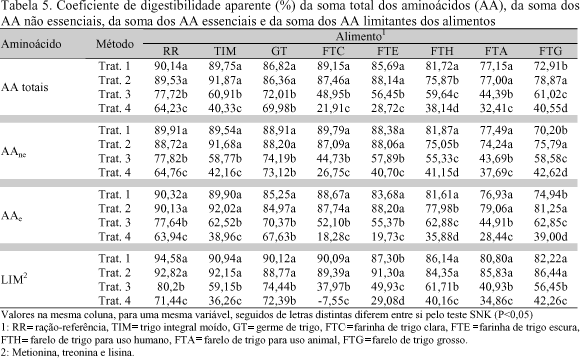
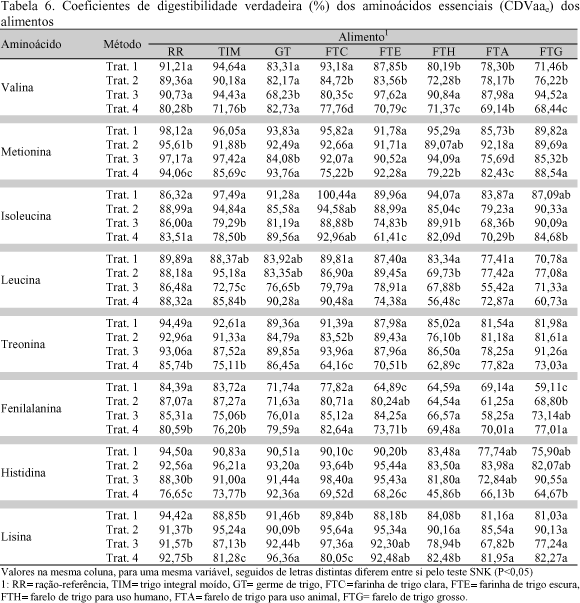
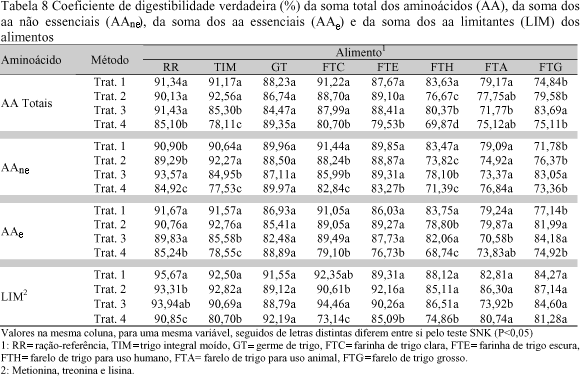
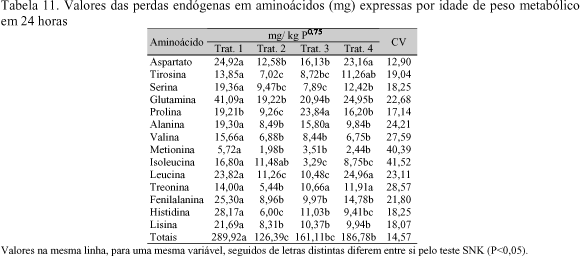
One experiment was run with broiler chickens to evaluate the coefficients of digestibility of amino acids (coefficients of apparent digestibility of amino acids - CDAaa and coefficients of true digestibility of amino acids - CDVaa) using wheat grain and some of its by-products, comparing four methodologies. The experiment was a completely randomized factorial design 4×8 (treatments × feedstuffs) with four replicates. Seven wheat grain by-products were used: wheat grain, wheat germ, white wheat flour, dark wheat flour, wheat bran for human use, wheat bran for animal use and rough wheat bran. Treatments 1 and 2 were the traditional methodology with ad libitum feed consumption, just differing in the age of the birds, 13 and 39 day-old, respectively. The feed tested substituted 40% of a reference diet. Feed intake and total excreta were recorded. The forced feeding method was used (Sibbald, 1976) for treatments 3 and 4. The birds were fasted 30 hours and forced fed 25g of the feed ingredients. In all the experiments a treatment was included with fasting birds to determine metabolic and endogenous losses. In method four caecectomized birds were used. Feeds and excreta were analyzed for dry matter, protein and amino acids. The traditional methods showed higher CDAaa values when compared to the forced feeding methods. For white wheat flour and dark wheat flour these values were negative, showing that endogenous losses were larger than amino acid intake. High fiber feedstuffs (wheat bran for human use , wheat bran for animal use and rough wheat bran) showed the lowest CDAaa and CDVaa values in the traditional and forced fed methods, confirming the interference of crude fiber on amino acid digestibility. In regard to the CDVaa, differences were smaller when compared the traditional and the forced fed methods, however, caecectomized birds showed lower CDAaa, due to high metabolic and endogenous losses.
bird; digestible amino acid; caecectomy