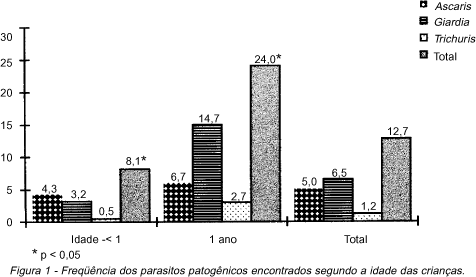
From March to May 1991, the prevalence of intestinal parasites was detected in 208 children under two-year old, from out patients attending the Public Health Service in Rio de Janeiro. Maternal parasitic infection was simultaneously investigated. Information regarding nurseling's breast-feeding and enteroparasites rates was also recorded. The centrifugal-sedimentation was the method used for stool analysis. Positivity was observed in 12.7% for children and 37.3% for women. Ascaris lumbricoides was the most frequently detected parasite in children under one-year old (4.3%) and mothers (12.7%). The distribution of parasites accordingly to breast-feeding showed a significant statistical difference (p < 0.05) among infants. No exclusively suckled child presented infection. Children whose mothers were infected showed almost two fold risk of infection (1.7). A correlation between enteroparasites and weaned children was observed (r = 0.75). We believe that infected mothers can contribute for parasitic infection of their kids.
Intestinal parasites; Breast-feeding; Infants; Epidemiology