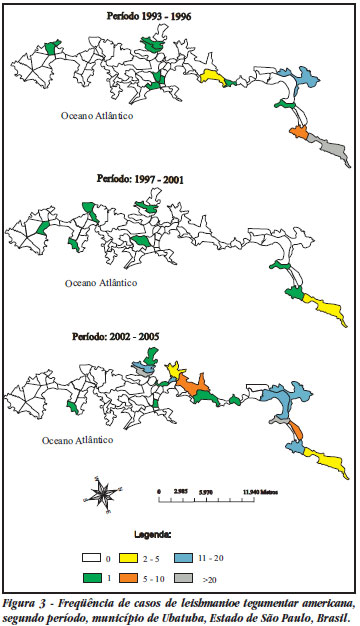
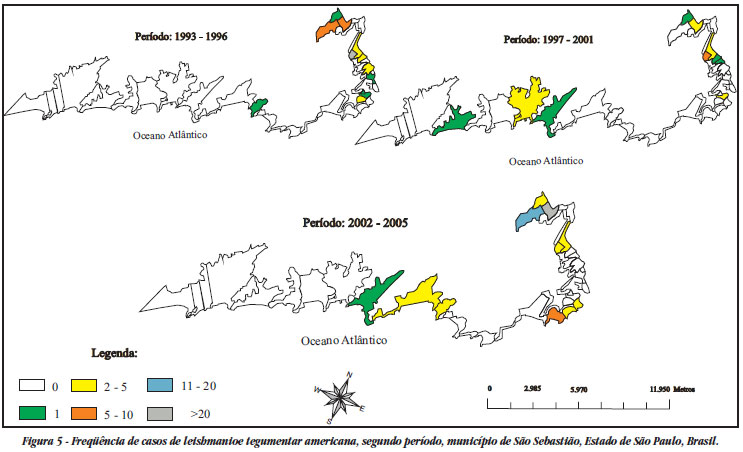
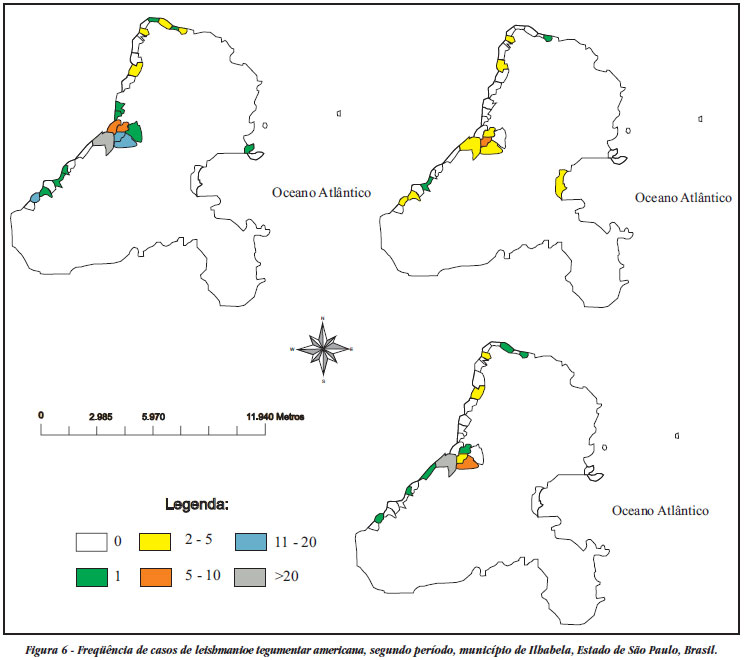
American cutaneous leishmaniasis acquired epidemic characteristics on the northern coastline of the State of São Paulo beginning in the 1990s. From secondary data, a descriptive study of the disease in the four municipalities making up this region over the period from 1993 to 2005 was conducted. The frequency of phlebotomine capture in the probable transmission locations was analyzed. 689 autochthonous cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis were notified, with single and grouped cases, thus determining that the spatial distribution was heterogenous. There was synchronism and cyclicity of disease manifestation, at intervals of six to eight years. All ages were affected, with slight predominance among males, without association with any specific occupation. Among the 2,758 phlebotomines captured, Nyssomyia intermedia predominated (80.4%) inside homes and in areas surrounding them. The disease presented a transmission profile inside homes and in areas surrounding them, between the urban fringe and forests, and inside forests. In such cases, transmission would be more related to enzootic foci.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis; Spatial analysis; Epidemiology; Phlebotominae; Geographic information systems