Abstract
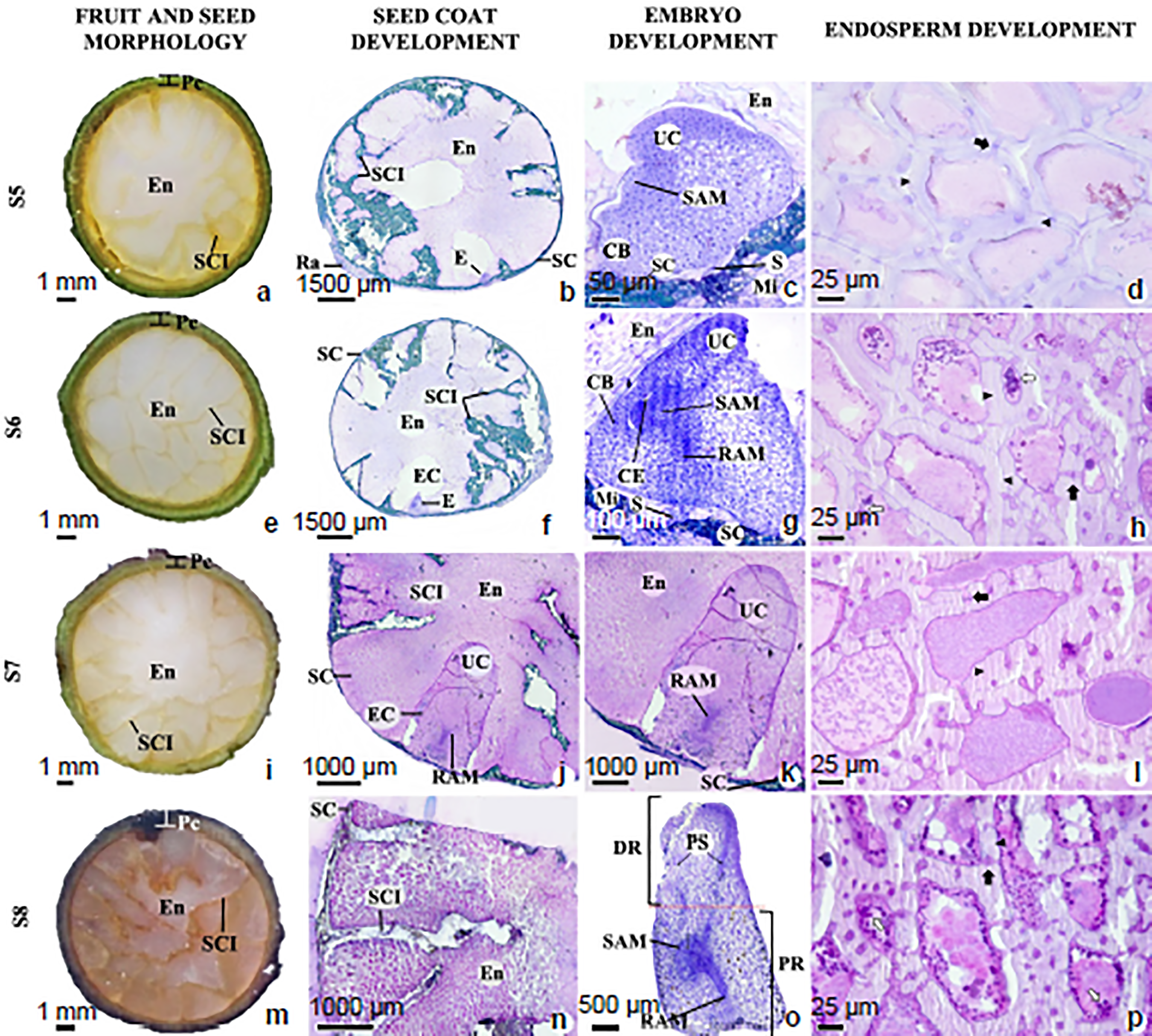
Although the consumption of açaí (Euterpe oleracea) pulp has long been an important component of the diet of the peoples from the Amazon, the açaí palm tree has recently attracted economic and scientific interest because of its vast array of bioactive compounds found in the fruit pericarp. The açaí seeds are the largest byproduct after pulp extraction and have potential for use in ethanol production, but this process is hindered by limited knowledge of seed biology, chemical composition and pattern reserve deposition during seed development. The aim of this work was to describe the morphoanatomical development of the seeds, as well as to identify the main organic compounds stored in the seeds. To achieve this goal, histological and histochemical analyses were performed on developing seeds. Results showed the seed is albuminous, bitegmic and that ingrowths of the seed coat give rise to a ruminate endosperm. Moreover, the nutritive reserves of açaí seeds are found in the endosperm thickened cell walls as reserve polysaccharides. Our findings provide information for future studies dealing with reproductive biology, propagation and the improvement of this profitable crop.
Key words:
embryogenesis; hypostase; pachychalaza; palm trees; ruminate endosperm

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail