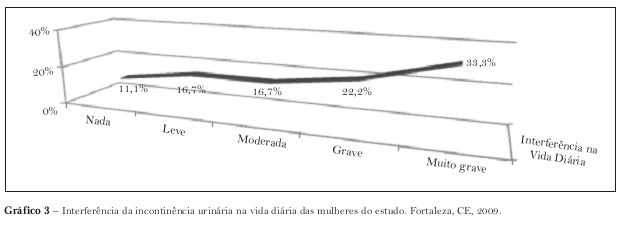
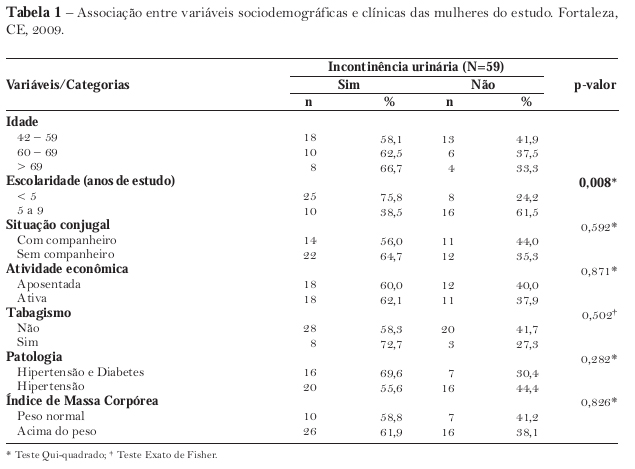
This study investigates the prevalence of urinary incontinence and how it interferes in the daily life of women from a health center in the city of Fortaleza, state of Ceará, Brazil. This is a cross-sectional, analytical and quantitative study. The studied population was of 168 women who had appointments for hypertension and / or diabetes in September 2009. The data was collected through interviews and the application of the "International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire." For inferential analysis, we used chi-square and Fisher's exact test. Women from the analysis sample (59) were: aged between 42 and 59 years (52.5%), low educational level (55.9%), without a partner (57.6%), retired (50.8%), nonsmokers (81.4%) and overweight (71.2%). Only the low educational level was associated with incontinence. Prevalence was of 61.0%. For 55,5% of incontinents, losing urine intervenes in a grave or very grave way with their daily life. The urinary loss occurred while coughing or sneezing (72.2%) and before arriving at the bathroom (61.1%). The urinary incontinence presented a high prevalence, intervening negatively with these women's lifes.
Urinary incontinence; Family Health Program; Public health