Abstract
Rice is a staple food in the Brazilian diet, but the slow consumption growth has a direct impact on the sector's expansion. In order to understand the factors affecting this consumption and their interrelationships with other food, this paper estimated the elasticities of demand for ten types of food in Brazilian households using microdata of the Household Budget Survey 2008-2009. Therefore, we applied the Quadratic Almost Ideal Demand System model (Quaids) adjusted for censored consumption and endogeneity of total expenditures. The overall results indicate that the rice has elasticity expenditure less than the unity. The income elasticity of demand reinforces this necessary good behavior, being higher in regions like the Midwest and Southeast. It also indicates that beans are complementary to rice, while bread and cassava flour are important substitutes. Finally, these results may be useful to boost household consumption of this product, through strategies that reduce its price, with the productivity increase or tax changes, or strategies focused on regional markets and to promote the substitution of other foods by rice.
Key-words:
Quaids model; rice; household demand; elasticities

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Fonte: Elaboração própria a partir dos microdados da POF 2008-2009.
Fonte: Elaboração própria a partir dos microdados da POF 2008-2009.
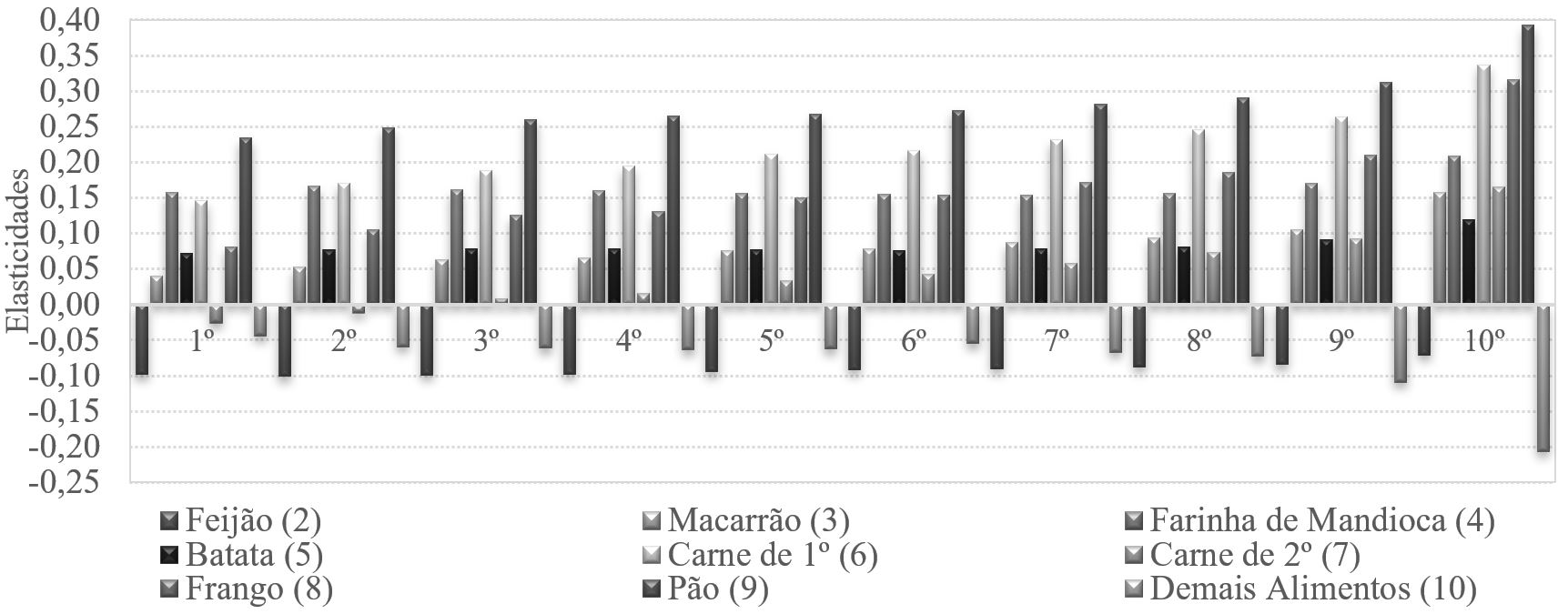 Fonte: Elaboração própria a partir dos microdados da POF 2008-2009.
Fonte: Elaboração própria a partir dos microdados da POF 2008-2009.
 Fonte: Elaboração própria a partir dos microdados da POF 2008-2009.
Fonte: Elaboração própria a partir dos microdados da POF 2008-2009.