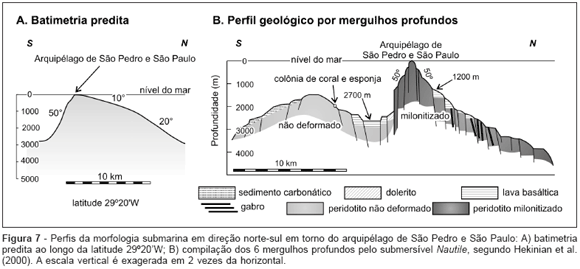
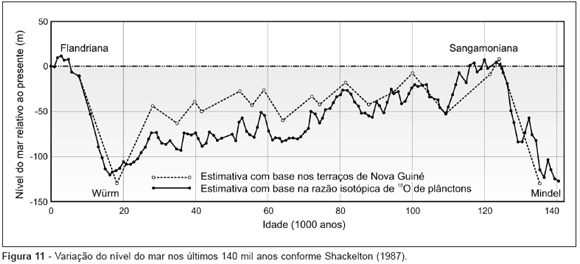
The Saint Peter and Saint Paul Islets are situated in the Equatorial Atlantic Ocean at the top of a submarine ridge made up of mantle peridotite. It is 90 km long, 25 km wide, and 3,800 m high, and is called the Saint Peter Saint Paul Peridotite Ridge. The submarine morphology is highly rugged with hundreds-of-meters-high scarps, suggesting the occurrence of probably recent active tectonism. The summit level map shows two surfaces of wave-cut benches with respective altitudes of 4~5 m and 7~9 m. The wave-cut benches are observed on three major islets in the same altitude ranges, indicating that no tilting or differential uplifting between the islets has occurred. Considering the upper platform to be formed during the Flandrian Transgression and the lower one developed by a recent erosive process, the mean uplift rate in the last 6.000 years is calculated to be 1.2~1.5 mm/year. The 14C datings for the coral fossils collected from the Belmont Island indicate the uplift rate in the last 6600 years to be 1.5~1.8 mm/year. Therefore, a rate of 1.5 mm/year should be reasonable for the present-day uplifting. Interpreting the peridotite ridge as a tectonically deformed megamullion, the total uplift would be 1500~3000 m and the tectonism should have started at 1~2 Ma. If the Peridotite Ridge is originated from the subcrustal oceanic mantle, the total uplift would be approximately 9000 m and the tectonism would have started close to 6 Ma.
Saint Peter Saint Paul Islets; tectonic uplift; wave-cut bench; summit level map; palaeogeomorphology