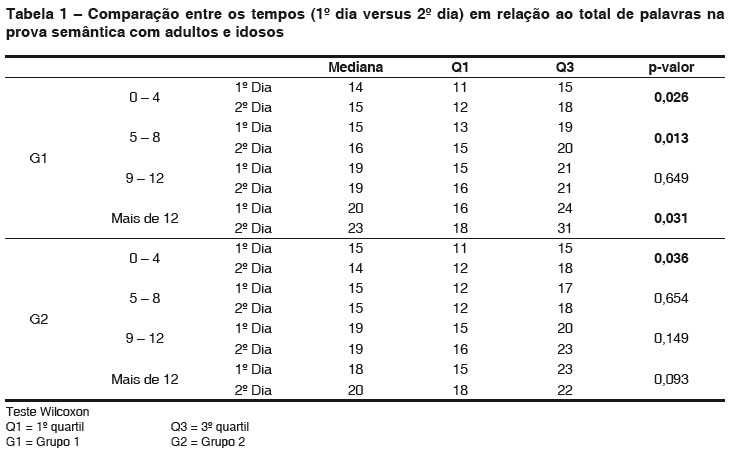
PURPOSE: to check verbal learning in normal subjects submitted to a verbal fluency test, considering age, schooling and sex. METHODS: 200 subjects, from 40 to 80-year old, submitted to a semantic and phonologic verbal fluency test, 1 minute long, taking place twice in a 24 hours period. RESULTS: after longitudinal analysis of the data obtained from the semantic test (1st day versus 2nd day) G1 indicated verbal learning in all schooling levels, except from 9 to 12 years of schooling. For G2 the level from 0 to 4 years of schooling was significant. In phonologic test G1 indicated verbal learning in all schooling levels, except from 9 to 12 years of schooling. And for G2, the level from 5 to 8 years of schooling was significant. Transversal analysis of the data (G1 versus G2) indicated no significant semantic test results and considering the phonologic test, just the second day was significant, observing the subjects from 0 to 4 years of schooling. Comparing both genders, among all groups and combinations of days, considering the semantic test, G1 gave evidence of significant data during the first and the second day. CONCLUSION: both tests attest that verbal learning was more effective for adults than for elderly people. However, there were no significant statistical differences among all groups, except from a decrease in words creation as long as age increased and schooling decreased. By comparing both genders, men performance improved in the semantic test.
Verbal Learning; Language; Adult; Aged