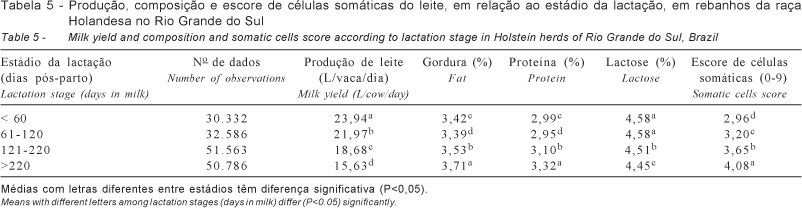
The effects of some environmental factors on milk yield and milk chemical composition and also on somatic cells count in dairy herds assisted by cooperatives (DHI) in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil were investigated in this trial. Data were obtained from a 5-year period of dairy control program totalizing 165,311 observations and were used to investigate the effects of year and month of dairy control, age at calving, time of farm on dairy control and stage of lactation on milk yield and composition. Milk yield including all observations averaged 19.36 L/cow/day. Greater milk yield was observed in cows varying from 5 to 6 years of age at calving, at the first 60 days of lactation, in the winter months and in herds with longer time in dairy control. Increased somatic cells count was associated to reduction in milk yield. Lower contents of milk fat and milk protein and greater somatic cells number were observed at the first 60 days of lactation. Concentration of milk lactose decreased with both the increment in somatic cells count and age at calving. Somatic cells count increased as the age of cows advanced and as lactation progressed. Milk contents of protein, fat and lactose all increased during the winter months possibly because of feeding temperate grasses. Results from this study showed that is important taking into account the effects of environmental factors on milk composition.
environment; milk composition; somatic cells; southern Brazil