ABSTRACT
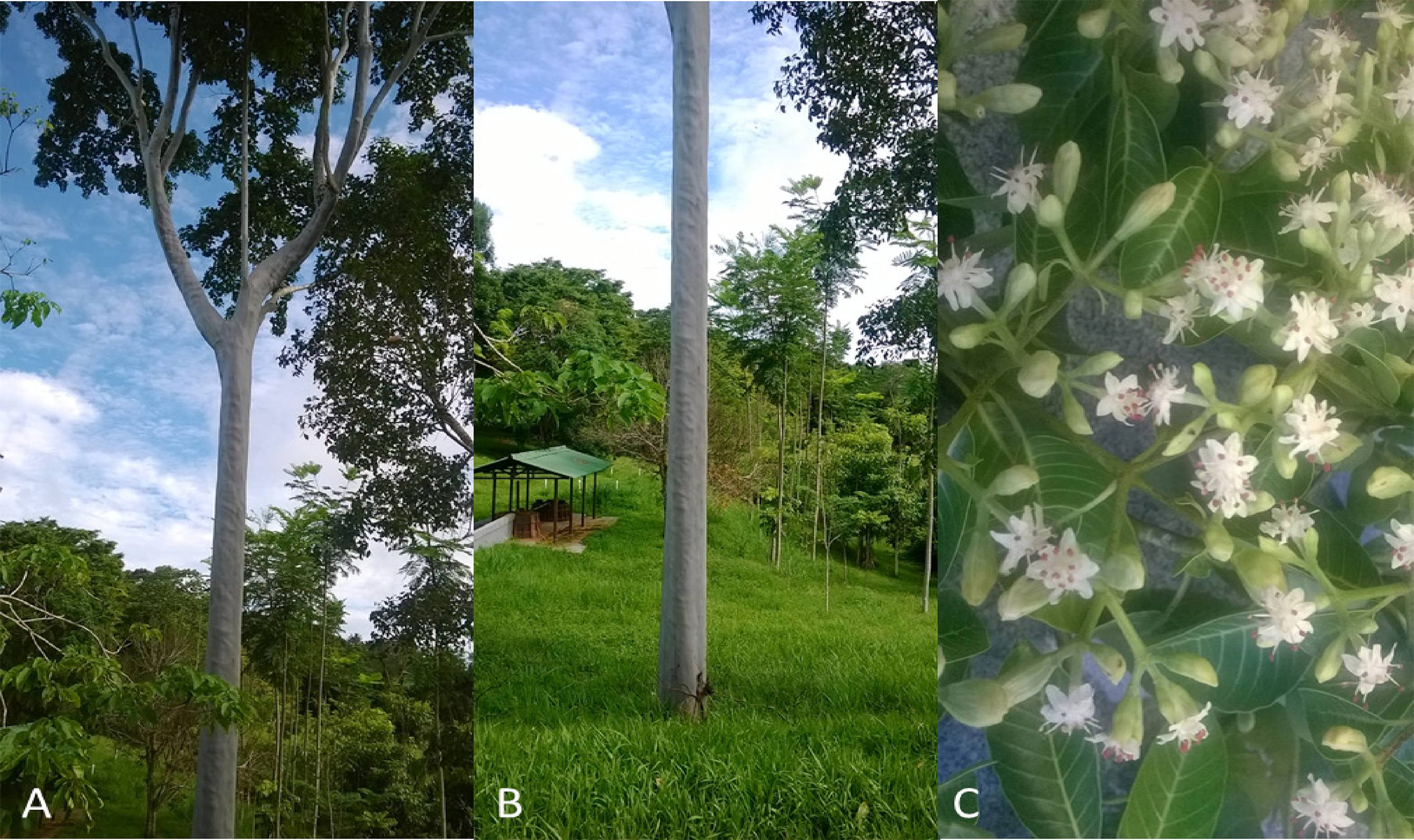
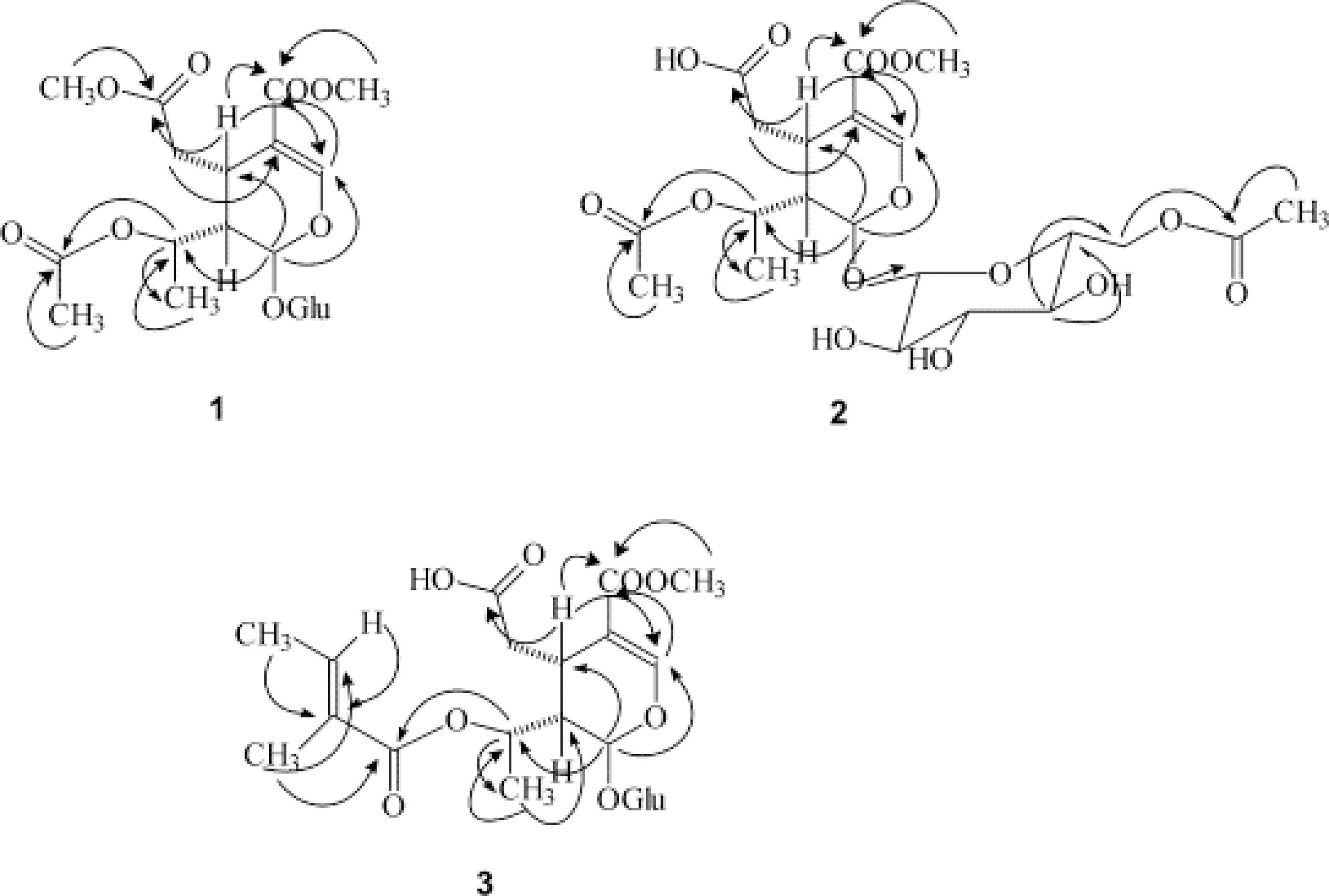
The Amazonian environment is a constant target for biopiracy and predatory extraction of resources due to the species with vast economic potential. Many of these species have not even been cataloged, and yet are already at imminent risk of extinction. In this paper, Calycophyllum spruceanum (Benth.) Hook. f. ex k. Schum., an Amazonian Rubiaceae, is studied with information on its botanical characteristics, ethnopharmacological uses, and chemical properties. Popularly known as mulateiro, the species is often prescribed in ethnomedicine for healing and vitality, and is also used to control skin patches. As a botanical peculiarity, it has a thin green epidermis that evolves into a dark brown periderm, which is renewed annually. In terms of chemistry, there is emphasis on the presence of alkaloids, tannins, and, especially, secoiridoids (7-methoxydiderroside, 6′-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyldiderroside, and 8-O-tigloyldiderroside are peculiar to the species). Even with proven photoprotective properties, research on C. spruceanum is still lacking, in particular studies aimed at the ex situ production of the plant and those that show the relationship between the plant’s ecology and the production of functional metabolites for the industry.
Keywords
Rubiaceae; mulateiro; predatory extraction