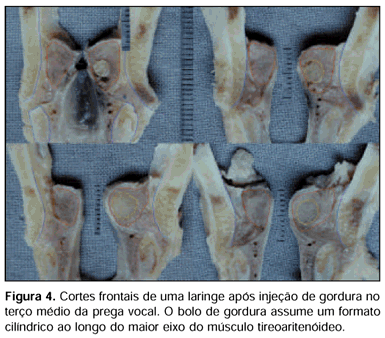
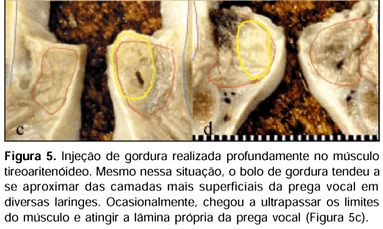
Intracordal fat injection has been used for vocal fold medialization in cases of laryngeal paralysis with variable results. A lack of consensus among the authors concerning various technical aspects, such as the site of injection, may contribute, in part, to this variation. AIM: To study the effects of the place of fat injection on the spatial distribution of fat and the configuration of the glottis after the injections. STUDY DESIGN: Experimental. MATERIAL AND METHOD: Six adult excised larynges were used. Fat harvested by liposuction was injected with a high-pressure syringe in the middle point of the vocal fold in three larynges and lateral to the vocal process of the arytenoid in another three. Digital photographs from a cranial view of the glottis were obtained before and after the injections. After fixation and decalcification, the larynges were cut in the frontal plane at the anterior, middle and posterior thirds of the vocal fold and at the level of the arytenoid cartilage in order to study the distribution of fat. RESULTS: Closure of the posterior glottis was observed only when fat was injected lateral to the vocal process of the arytenoid. Fat tended to occupy a cylindrical space inside the thyroarytenoid muscle, along the longer axis of the vocal fold, even when injected close to the vocal process of the arytenoid. CONCLUSION: The place of fat injection influenced the configuration of the glottis after injection, although the fat tended to occupy a cylindrical space along the longer axis of the vocal fold in both groups.
vocal cord paralysis; larynx; voice disorders