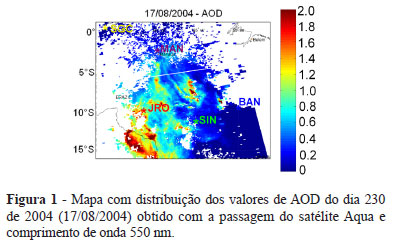
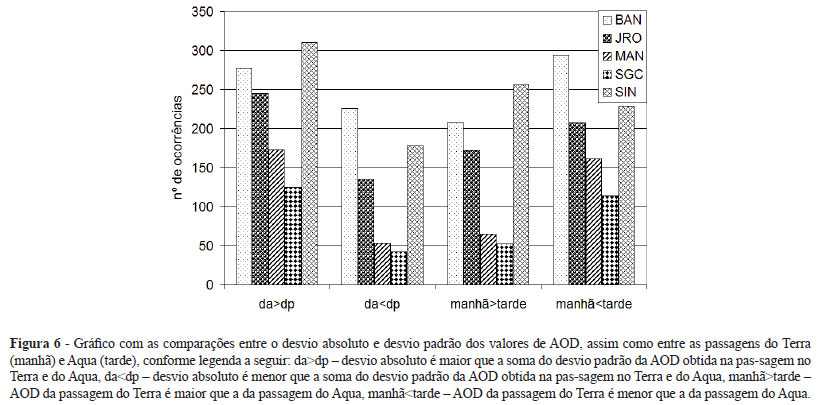
A study of the temporal and spatial variability of the aerosol optical depth (AOD) and its spatial homogeneity was performed in order to describe and quantify the AOD at five locations at the Amazon region, four of them present strong influence of biomass burning emission, using a long time series of data. Data were obtained from the MODIS sensor (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer), onboard the Terra and Aqua satellites, from 2000 to 2011. Spatial analysis was performed to verify the homogeneity of the AOD values. Mean AOD values were calculated for distinct area sizes and a study of the diurnal and annual variability was performed. Mean AOD presented little variation with increasing area, indicating that the aerosol layers are very well mixed. Annual AOD average fluctuations showed similar behavior in the sites of the deforestation arc. A similar behavior was observed in Manaus only during drier years, and São Gabriel da Cachoeira presented only low AOD values, meaning that this portion of the Amazon region is not affected by smoke plumes (AOD between 0,1-0,2). Comparing morning and afternoon data periods, the number of days with higher AOD values in the afternoon was higher, probably because burnings occur mainly during the afternoon. Periods of high AOD values (AOD between 1-3) lasted from the end of the dry season to the beginning of the rainy season, and the estimated duration was between 69 and 79 days.
aerosol optical depth; Amazon burning; atmosphere remote sensing