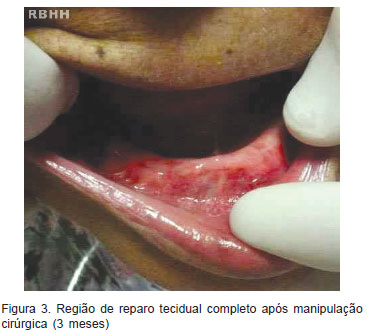
The use of bisphosphonates among patients affected by osteolytic diseases, such as multiple myeloma, metastatic bone lesions and osteoporosis has been associated with the risk of osteonecrosis of the jaws. Bisphosphonates are found in areas of the bone that are undergoing inflammation or resorption. They are phagocytosed and internalized by osteoclasts. Once in the bone, these bisphosphonates cause apoptosis or cell death of the osteoclasts and as a result they may inhibit osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. Bisphosphonates seem to affect osteoclasts when it comes to both numbers and function. Although bisphosphonates are potent and valuable inhibitors of osteoclastic bone lesions, several unanswered questions exist regarding the risk of developing osteonecrosis and the management of this complication. This study reports two clinical cases of osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with the use of bisphosphonates. According to the findings, the two patients (women) with different neoplasms: multiple myeloma and breast cancer with metastatic bone lesions presented some signs and symptoms of osteonecrosis.
Osteonecrosis; bisphosphonates; maxillary diseases