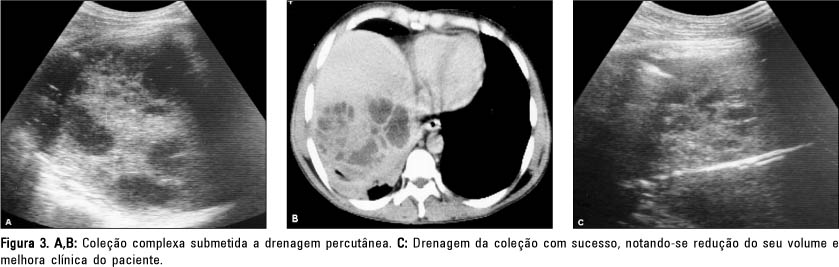
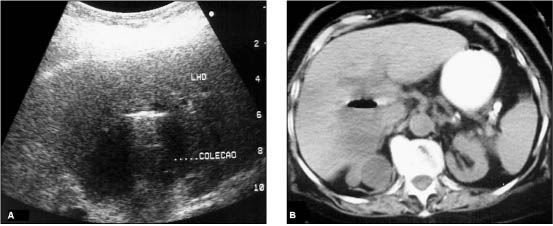
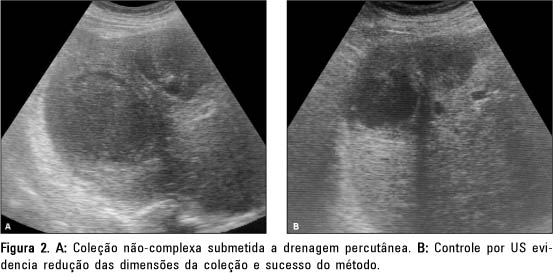
OBJECTIVE: To determine and compare the efficacy of percutaneous needle aspiration and percutaneous catheter drainage, both guided by imaging methods, for the treatment of liver abscesses. MATERIALS AND METHODS: From 52 patients referred to our service for percutaneous treatment of abdominal abscesses, 17 presented liver abscesses, 13 of which were considered noncomplex and four were considered complex (multiloculated, multiple or associated to fistulas). Percutaneous needle aspiration was performed in 7/17 patients and 10/17 patients were submitted to percutaneous catheter drainage. The method used was considered successful when there was complete abscess resolution with both clinical and laboratorial improvement. RESULTS: The procedures were successful in 82.4% of all cases. In the group submitted to percutaneous needle aspiration the rate of success was 57.1% and in the group submitted to percutaneous catheter drainage the rate of success was 100%. Successful treatment was achieved in 75% of the patients submitted to percutaneous needle aspiration for abscesses smaller than 100 ml, but in only 33.3% of the patients with abscesses between 100 and 250 ml. There was complete resolution of the abscesses with percutaneous needle aspiration in 75% of the simple abscesses and in 25% of the complex abscesses. CONCLUSION: Percutaneous catheter drainage is more effective than percutaneous needle aspiration for the treatment of liver abscesses. Needle aspiration may probably be used as a valid alternative for smaller and noncomplex abscesses.
Liver abscesses; Percutaneous needle aspiration; Percutaneous catheter drainage