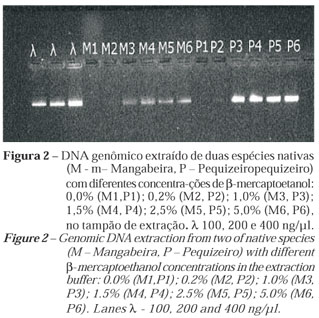
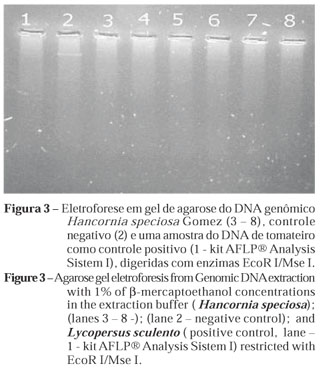
Great amounts of contaminants in DNA samples hamper the extraction of high-quality genomic DNA. The main problem is the presence of polysaccharides, phenols and other secondary metabolites that impair the DNA isolation procedure and subsequent application, by inhibiting the Taq DNA polymerase and restriction enzyme activity. This study describes a modified procedure based on hexadecyltrimethylammonium (CTAB) from which genomic DNA, ap-propriate for subsequent manipulation such as PCR reactions and restriction enzyme diges-tion, is derived. This protocol uses different β-mercaptoethanol concentrations in the extrac-tion buffer ( 0.0; 0.2; 10 ; 15; 25 and 50 uL β-mercaptoethanol/ml from the extraction buffer: 100mM Tris-HCl, pH 8 ; 20 mM EDTA, 1.4 M NaCl ; 2% CTAB; 1% PVP ). The procedure was tested on mature leaves of Annona crassiflora (araticum), Eugenia dysenterica (cagaita), Anacardium humilis (caju-do-campo), Hancornia speciosa (mangaba) e Caryocar brasiliensis (pequi ).The protocol was efficient in the isolation of polysaccharide and polyphenol-free DNA of high molecular weight using β-mercaptoethanol concentrations of over 1 % in the extraction buffer. The purity of thereby isolated DNA isolated was high according to the di-gestion analyses by PCR restriction and amplification.
Annona crassiflora (araticum); Eugenia dysenterica (cagaita); Anacardium humilis (caju-do-campo)