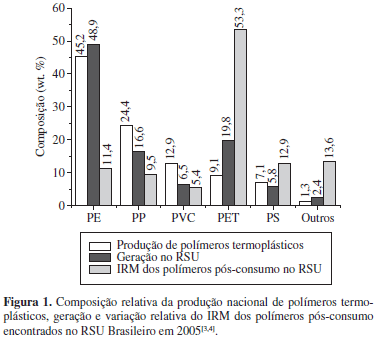
We present a review on poly(ethylene terephthalate), emphasizing the synthesis processes and the degradation mechanisms. Brazil is currently among the countries that most recycle PET, with 53% of this polymer being mechanically recycled. The success of this thermoplastic in the recycling industry is due to its large diversity of applications, from the textile industry to food packaging, where the food grade recycled packages will be mixed with the pristine resin for reprocessing and use. We also discuss the present legal aspects concerning PET recycling and its use in contact with food. In the synthesis of PET, usually done in two or three steps, several co-monomers and additives are used to optimize the final properties and processing conditions. Additionally, during the synthesis, processing and recycling, several degradation (thermomechanical and thermo-oxidation) and secondary reactions occur, producing acetaldehydes, oligomers and diethyleneglicol. The presence of these "contaminants" accelerates the degradation process of the polymer affecting the final product characteristics.
Acetaldehyde; diethylene glycol; oligomers; poly(ethylene terephthalate); thermomechanical degradation; thermo-oxidation degradation