Abstract
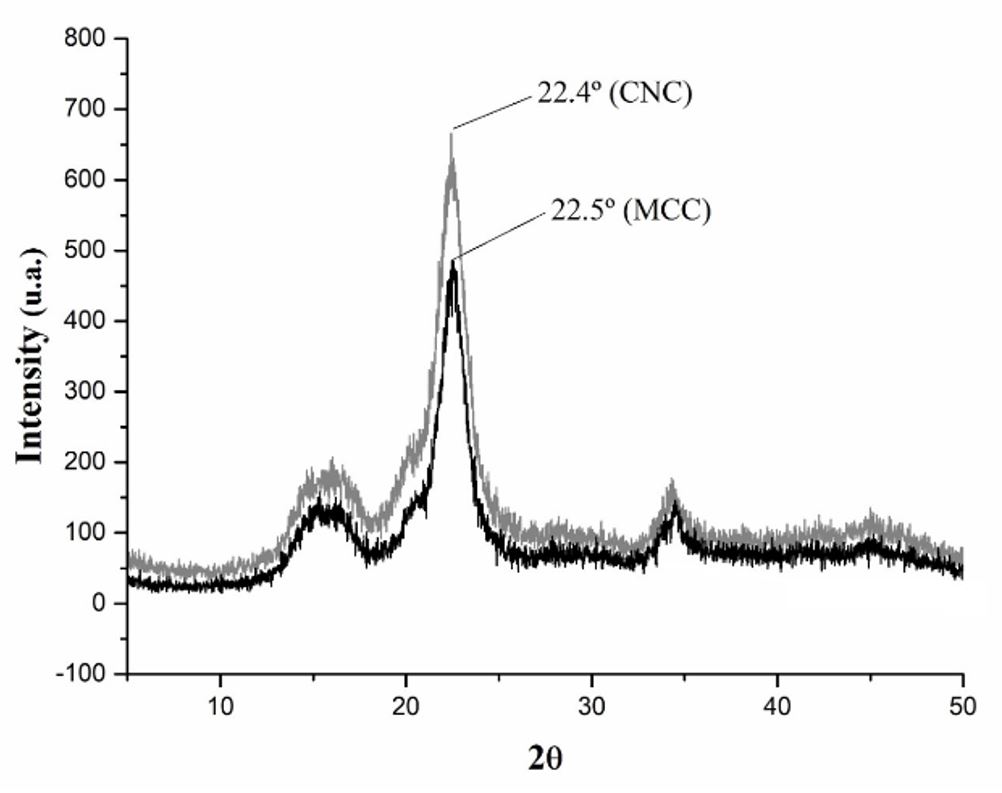
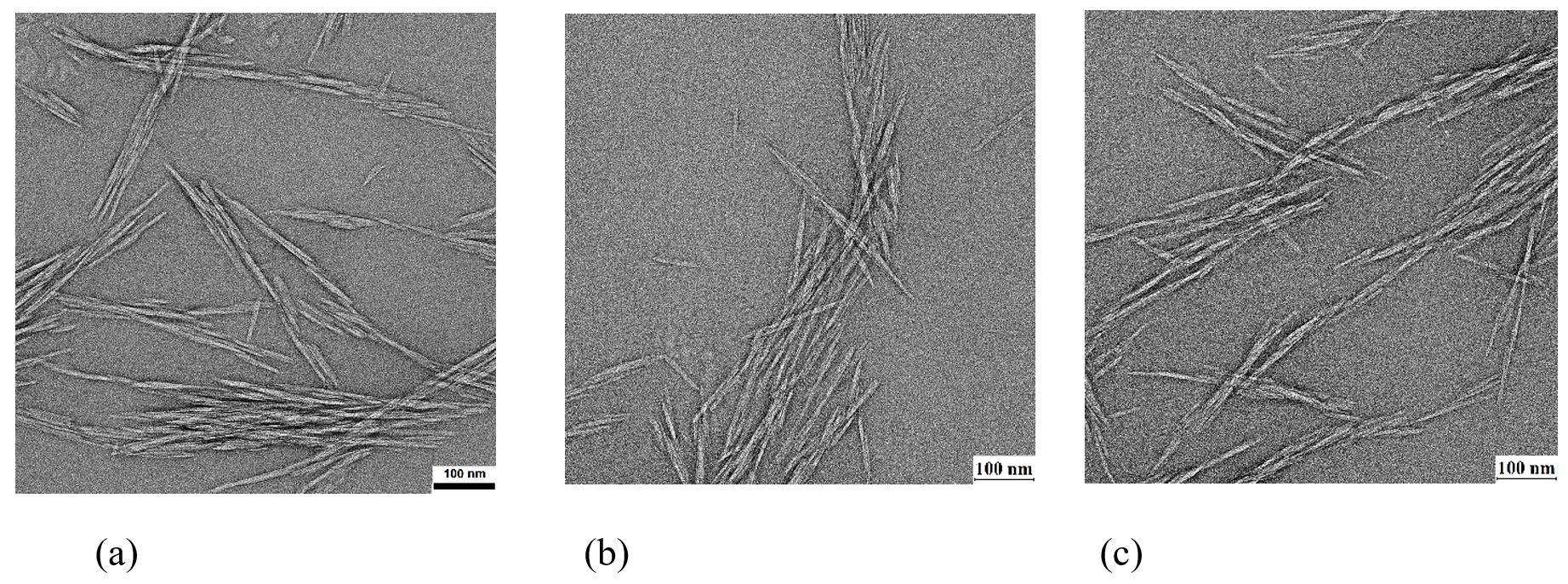
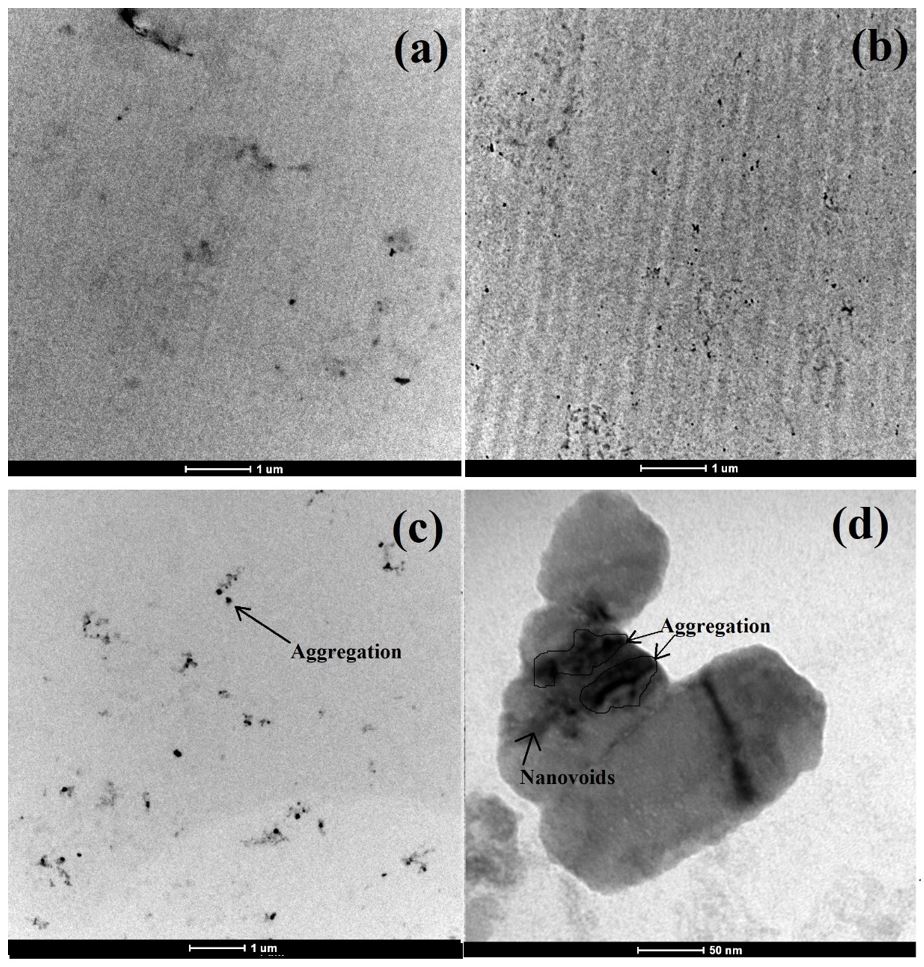
This study evaluated the influence of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) content on the properties of epoxy nanocomposites. The CNC were obtained from microcrystalline cellulose by acid hydrolysis. 4.0, 5.5 and 7.0% of untreated CNC were incorporated into epoxy resin. Sonication was used to disperse the CNC in the resin. The thermal stability, the glass transition temperature and the degree of conversion were reduced as observed by Thermogravimetry and Differential Scanning Calorimetry, respectively. The tensile and bending modulus showed no significant improvement and the impact resistance showed a slight reduction due to the non-uniform dispersion of the CNCs, as observed by Transmission Electron Microscopy. Analysis of Scanning Electron Microscopy showed a change of the fracture mechanism of the epoxy resin: the CNCs increased the elastic modulus by reinforcement, but accelerated the fracture by acting as defects. The Halpin-Tsai model was applied to predict the elastic modulus of the epoxy/CNC system.
Keywords:
cellulose nanocrystals; nanocomposites; epoxy resin

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail