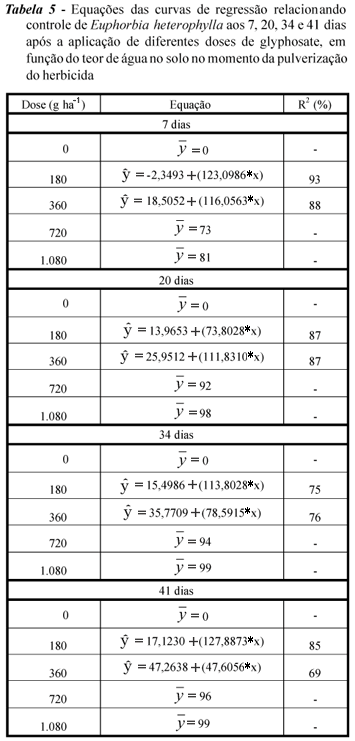
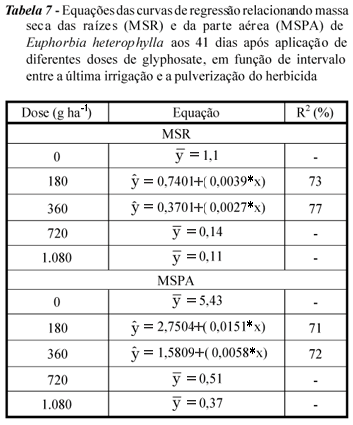
A greenhouse experiment was carried out to evaluate the efficacy of glyphosate in controlling Euphorbia heterophylla growing under different soil moisture levels and to determine the lowest soil moisture level failing to prevent herbicide effectiveness in controlling this weed. The experiments were arranged in a randomized block design in a 6 x 5 factorial scheme, corresponding to six intervals between the last irrigation and herbicide application (0, 6, 12, 24, 48 and 72 hrs) and five glyphosate doses(0, 180, 360, 720, and 1.080 g ha-1). When the plants achieved the 3-leaf pair stage, 10 mm of simulated rain were applied. At the end of the rain simulation period, the herbicide was applied using a pressurized backpack sprayer with CO2, using 120 L ha-1 of spray volume. On days 7, 20, 34 and 41 after application, the control was evaluated by using a visual scale as well plant height (cm) and on day 41, the dry weight of both the root and aerial part was assessed. Satisfactory control levels of E. heterophylla were verified at a dose of 720 g ha-1 glyphosate, regardless of the time interval between the last irrigation and herbicide application. Application of 360 g ha-1 of glyphosate at time intervals shorter than 48 hrs, between the last irrigation and its application and in soils presenting water contents higher than 0.09 cm³ cm-3, did not prevent herbicide efficacy. Application of 180 g ha-1 of glyphosate at intervals shorter than 12 hrs between the last irrigation and its application and in soils presenting water contents higher than 0.14 cm³ cm-3 did not affect herbicide efficacy.
EPSPs inhibitors; water deficit; weed