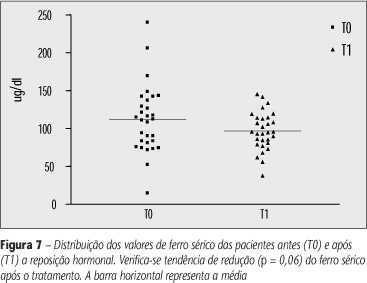
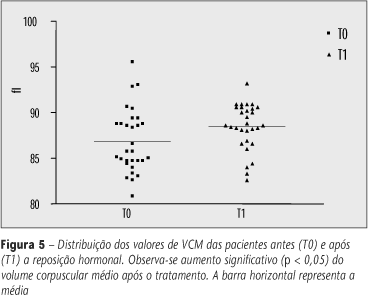
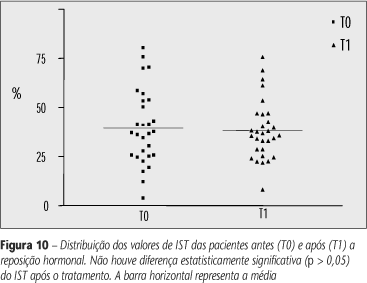
BACKGROUND: In literature there are many studies about iron status in children, adolescents and fertile women, but investigations of iron stores and erythrocyte parameters variation after hormone replacement therapy (HRT) are rare. Elevated iron stores, oxidative stress, and estrogen deficiency may place premenopausal and menopausal women in a risk of developing heart disease and cancer. OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the effect of HRT in erythrogram and iron status in premenopausal and menopausal women. METHODS: Hematological indices and iron status were assessed by erythrogram, serum ferritin, iron and transferrin iron-binding capacity (TIBC) in 30 pre- and menopausal women before and after HRT with medroxiprogesterone and estradiol. The blood exam, serum iron and iron-binding capacity were determined by laboratory classic methods, while ferritin was measured by quimiluminescent assay. RESULTS: HRT use was followed by a significant reduction in the absolute number of erythrocyte, an increase of hematimetric indexes and a trend towards a reduction of serum iron levels and TIBC. No alterations on serum ferritin and transferrin saturation index were detected after HRT. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: In the present study, alterations in red cell and iron parameters, which could impair the use of HRT in premenopausal and menopausal women, were not observed. Our results suggest that HRT in premenopausal women are beneficial to iron status, maintaining normal iron stores and promoting elevation of red cells indexes.
Ferritin; Iron status; Hormone replacement, therapy; Premenopausal