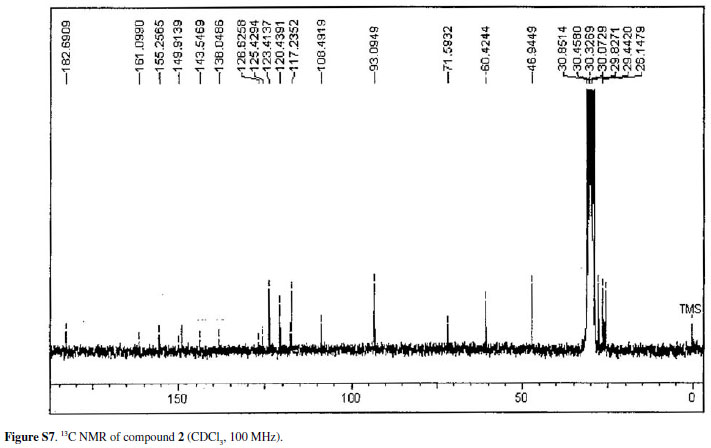
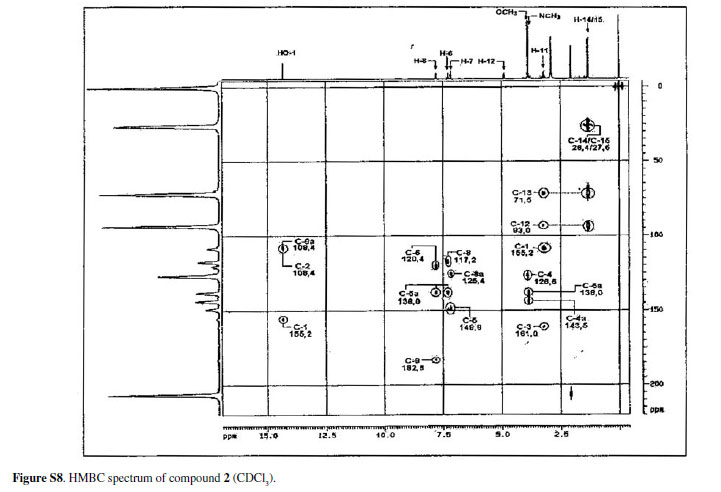
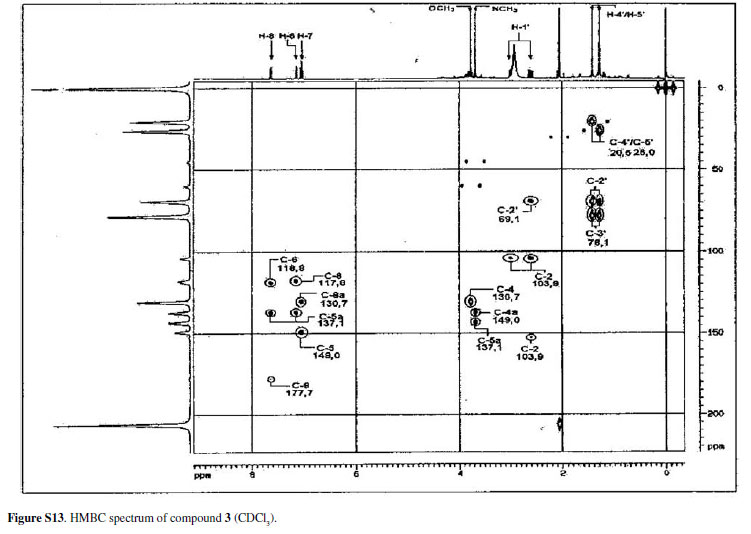
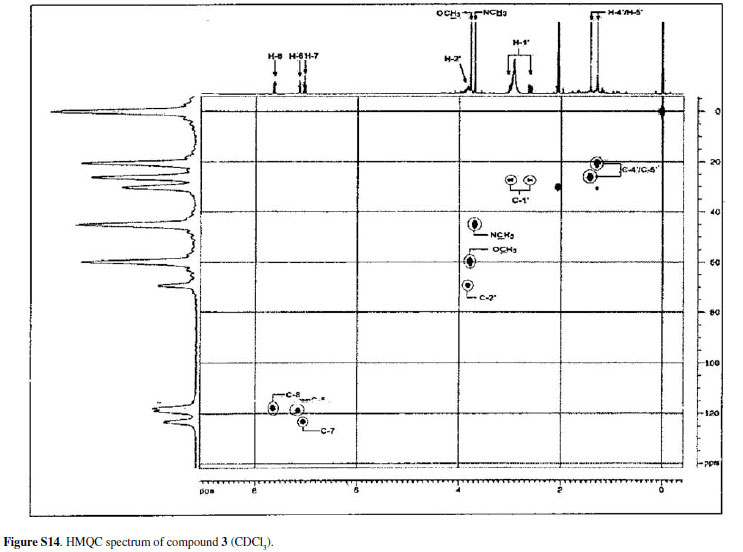
Eleven acridone alkaloids isolated from Swinglea glutinosa(Bl.) Merr. were examined for in vitroactivity against chloroquine-sensitive Plasmodium falciparum3D7, Trypanosoma brucei rhodesienseSTIB900 and Leishmania donovaniL82. An assay with KB cells was developed in order to compare in vitrotoxicity of alkaloids with the selective action on the parasites. Nine of the compounds had IC50 values ranging from 0.3 to 11.6 µM against P. falciparum. In contrast, a small number of compounds showed significant activity against T. brucei rhodesienseand none had activity against L. donovani. Among the alkaloids three had IC50 < 1.0 µM against P. falciparum, whereas against T. b. rhodesiensefive had IC50 < 10 µM. The characterization of the acridone alkaloids, 1,3,5-trihydroxy-4-methoxy-10-methyl-2,8-bis(3-methylbut-2-enyl)acridin-9(10H)-one (1), 2,3-dihydro-4,9-dihydroxy-2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-11-methoxy-10-methylfuro[3,2-b] acridin-5(10H)-one (2) and 3,4-dihydro-3,5,8-trihydroxy-6-methoxy-2,2,7-trimethyl-2Hpyrano[2,3-a]acridin-12(7H)-one (3), is discussed, as well as the structure-activity relationship of all compounds assayed. Isolation and spectral data of alkaloids 1-3are described for the first time although their citotoxicities to cancer cells have been described before.
antiparasitic acridone alkaloids; malaria; Swinglea glutinosa; Rutaceae