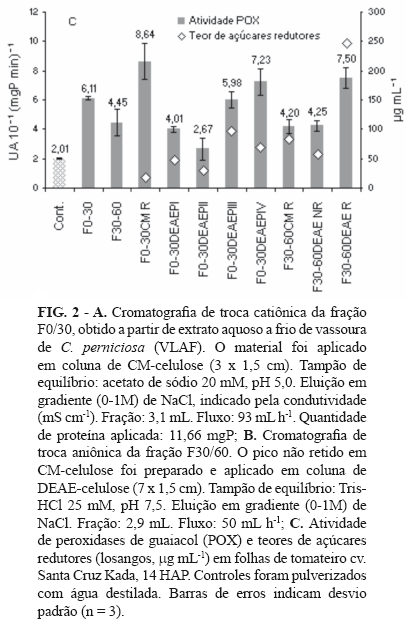
A crude formulation (VLAF) of an aqueous cold extract obtained from Solanum lycocarpum necrotic tissue infected by Crinipellis perniciosa was showed capable of reducing disease progress of tomato bacterial leaf spot, when previously sprayed on tomato plants. The fractions F0/30 and F30/60 were achieved by saline precipitation and they showed highest amounts of proteins from VLAF. The fractions were submitted to cationic exchange chromatography for protein scanning. Non-retained peaks from this first chromatography were submitted to an anionic exchange chromatography. Both retained and non-retained peaks from both ion exchanges were sampled and sprayed on cv. Santa Cruz Kada tomatoes. Contrasting peroxidase activities were observed 14 hours after sprayings. The samples that produced the highest peroxidase increases were the retained peak in cationic exchange from F0/30 (F0-30CMR) and the retained peak in anionic exchange chromatography from F30/60 (F30-60DEAER). Our results indicate the viability of searching for protein- or carbohydrate-derived molecules from VLAF aqueous extract.
elicitor; protein fractioning; natural extract