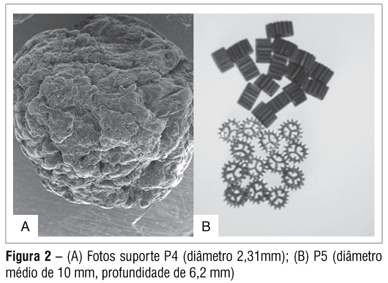
This paper presented the influence of material support kind: P4 (rugous recycled plastic, medium diameter of 2.31 mm, density of 900 kg.m-3, specific surface potential of 2,596 m².m-3sup) and P5 (polietilene, cilindric shape, medium diameter of 10 mm, density of 880 kg.m-3, specific surface potential of 3,075m².m-3sup) used in two continuous flux biological moving bed reactors using different material support to remove nitrogen and carbon from sewage, which was divided in two phases according to sludge retention time (SRT): phase A: SRT of 10 days and phase B: SRT of 3 days. The organic loading rates applied were 4.0 kgCOD.m-2.d-1 (P4) and 4.1 kgCOD.m-2.d-1 (P5); and the nitrogen loading rates applied were 0.63 kgN.m-2.d-1 and 0.66 kgN.m-2.d-1 for P4 and P5, respectively. The support P4 achieved efficiencies of 87% for total carbon removal and 83% for nitrogen removal during phase A. These efficiencies slightly decreased to 80 and 77% for total carbon and nitrogen, respectively (phase B). The support P5 got removal efficiencies of 63% for total carbon and 55% for nitrogen (phase A) and 59% for total carbon and nitrogen (phase B). These results showed that the total carbon and nitrogen removal efficiencies were not affected by the SRT, but by the kind of support used (carrier geometry or surface characteristics) and available specific surface area for biomass growth.
carbon; sludge retention time; support material; nitrogen; hybrid reactor; wastewater treatment