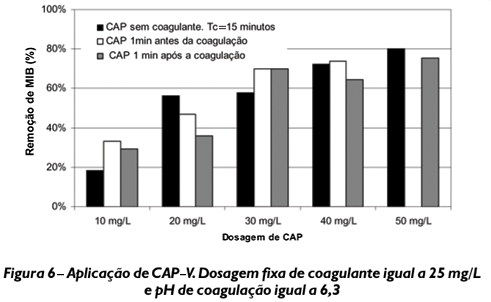
Powered Activated Carbon (PAC) has been widely used in Water Treatment Plants with the purpose of minimizing taste and odor problems in drinking water. Its application can be done immediately before or after coagulant application or in parallel with it. To look into possible interferences of the coagulation process in the adsorption process, an experimental investigation was carried out by means of jar tests, with the purpose of simulating different case scenarios of PAC and coagulant application. For the same PAC type and coagulant dosage, regardless of the application point, it was not observed any significant differences in the removal of taste and odor compounds, thus indicating that under the tested conditions the PAC application point has a much lower importance than the initially expected in adsorption processes.
Drinking water treatment; adsorption; taste and odor compounds; powdered activated carbon