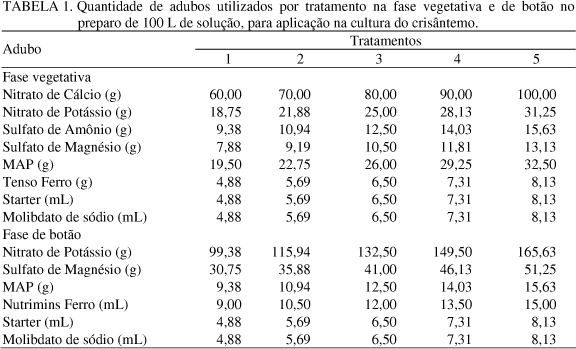
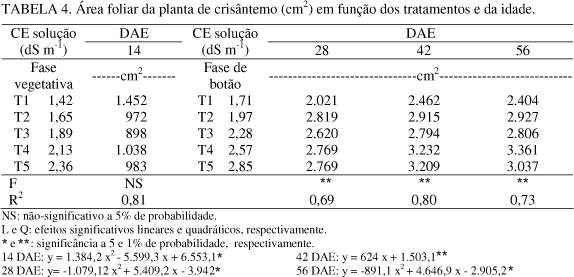
In floriculture market, the competition is intense and the productivity differential consists in an appropriated nutritional management which provides a large impact in quality, productivity and longevity of the flowers and plants. This present work aimed to evaluate the effects of electrical conductivity (EC) levels in chrysanthemum plant (Dendranthema grandiflora Tzvelev.) development. These plants were planted in pots and cultivated in a greenhouse. The experiment was carried out in Paranapanema city, São Paulo State. The experimental design was made in randomized blocks with four repetitions and split plots. The plots were constituted according to the sample times, and the split plots according to the different EC levels which were determined in the applied water irrigation solution: 1.42; 1.65; 1.89; 2.13 and 2.36 dS m-1 (vegetative stage); 1.71; 1.97; 2.28; 2.57 and 2.85 dS m-1 (bud stage). The plant height and the bouquet diameter were weekly evaluated, and every 14 days the leaf area and the dry mass of the aerial portion of the plant were measured. The treatment which applied the EC level of 2.13 dS m-1 during the vegetative stage and 2.57 dS m-1 during the bud stage provided the best visual aspect in plants, as well as the higher aerial part if the dry mass, higher leaf area and the best formation and coloring.
Dendranthema grandiflora; fertigation; greenhouse