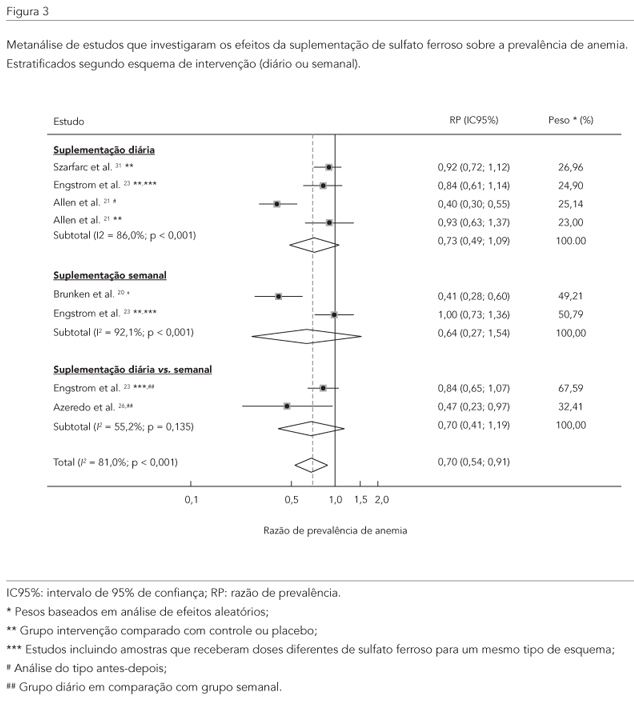
This was a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies evaluating the effectiveness of ferrous sulfate supplementation in the prevention of anemia in children under five. The database search included PubMed, Scopus, LILACS, and SciELO. Articles published between 1980 and 2011 in Spanish, English, or Portuguese were included, using the keywords child, preschool, infant, anemia, prevention, and iron supplementation. The authors selected 13 studies, which showed that regardless of dose and duration of supplementation, daily regimen was more consistently related to improvement in hemoglobin levels (pooled effect 0.56mg/dL, 95%CI: 0.31; 0.81, p < 0.001) as compared to weekly intervention (pooled effect 0.28mg/dL, 95%CI: -0.22; 0.78, p = 0.273). Iron supplementation was not associated with decreased prevalence of anemia, even with daily doses, and administration with other micronutrients did not bring additional benefits compared to the exclusive administration of iron supplement. Daily supplementation of ferrous sulfate was more effective than weekly doses in improving hemoglobin levels.
Anemia; Iron; Preschool Child; Dietary Supplements