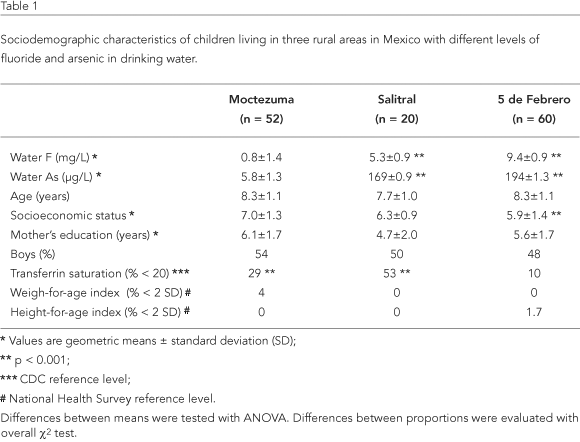
Recent evidence suggests that fluoride (F) and arsenic (As) may adversely affect intelligence quotient (IQ) scores. We explore the association between exposure to F and As in drinking water and intelligence in children. Three rural communities in Mexico with contrasting levels of F and As in drinking water were studied: Moctezuma (F 0.8±1.4mg/L; As 5.8±1.3µg/L); Salitral (F 5.3±0.9mg/L; As 169±0.9µg/L) and 5 de Febrero (F 9.4±0.9mg/L; As 194±1.3µg/L). The final study sample consisted of 132 children from 6 to 10 years old. After controlling for confounders, an inverse association was observed between F in urine and Performance, Verbal, and Full IQ scores (beta values = -13, -15.6, -16.9, respectively). Similar results were observed for F in drinking water (beta values = -6.7, -11.2, -10.2, respectively) and As in drinking water (beta values= -4.30, -6.40, -6.15, respectively). The p-values for all cases were < 0.001. A significant association was observed between As in urine and Full IQ scores (beta = -5.72, p = 0.003). These data suggest that children exposed to either F or As have increased risks of reduced IQ scores.
Fluorides; Arsenic; Potable Water; Neurotoxins; Intelligence