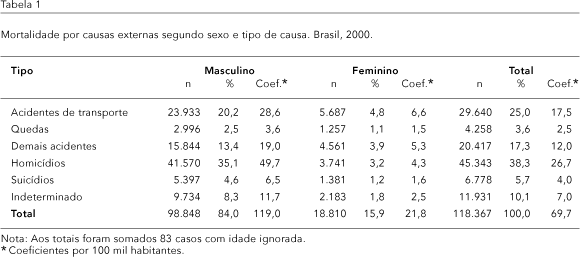
Since the early 1980s, external causes have been the second greatest cause of death in Brazil. They also place a growing demand on health care services. The current study analyzes morbidity and mortality from external causes in Brazil. The study material consists of 118,367 deaths and 652,249 hospitalizations due to external causes during the year 2000. The data are from the National Mortality Information System and Hospital Information System. The mortality coefficient from external causes was 69.7/ 100 thousand (119.0/100 thousand for males and 21.8/100 thousand for women). Homicides were the leading cause of death (38.3% of the total), with a high coefficient of 26.7/100 thousand, while falls were the leading cause of hospitalizations (42.8% of the total). Motor vehicle accidents were a major cause of both morbidity and mortality. Fractures, mostly occurring in the upper and lower limbs, accounted for 42.6% of hospitalizations. Based on the findings, preventive programs should aim to decrease both mortality and morbidity, with special emphasis on homicides, traffic accidents, and falls.
Violence; Mortality; Morbidity