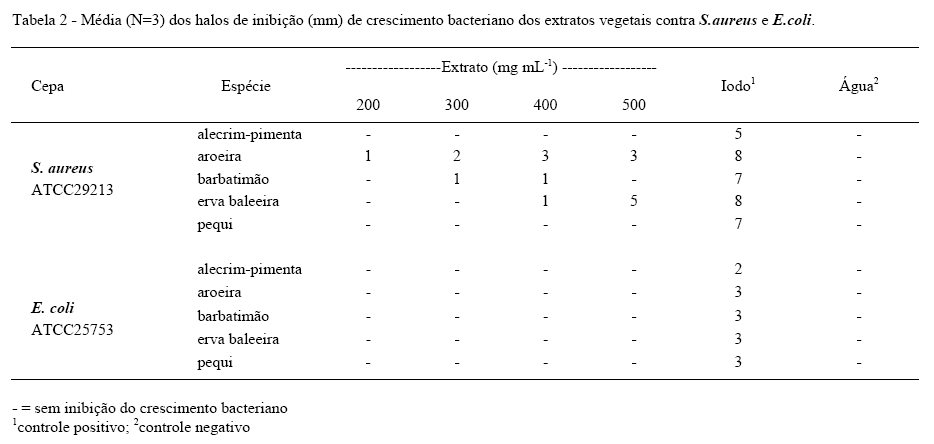
This study evaluated the phytochemical profile of standardized hydroalcoholic extracts (EAPs) obtained from leafs of rosemary (Lippia sidoides), peppertree (Myracrodruon urundeuva), barbatimão (Stryphnodendron adstringens), erva baleeira (Cordia verbenacea) and from the meal of pequi fruit peel (Caryocar brasiliense) and the activity of different levels of these EAPs against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. After collection and identification of the species, plant leaves and pequi peel were separated to prepare the EAPs. The EAPs underwent phytochemical screening. The antimicrobial activity of the EAPs at different dilutions (200, 300, 400 and 500mg mL-1) was tested using the disk diffusion method. The phytochemical screening detected components with antimicrobial potential in the EAPs tested. The disk diffusion test showed that peppertree (≥200mg mL-1), barbatimão (≥300mg mL-1) and erva-baleeira (≥400mg mL-1) extracts inhibited S. aureus growth, but not E. coli development. The EAPs did not affect E. coli development, but the leaves from peppertree, barbatimão and erva-baleeira exhibited potential to inhibit S. aureus growth. The leaves and bark of the studied plants may consist in a sustainable, affordable and feasible alternative to treat microbial infections.
phytoterapy; alcoholic extract; microbial susceptibility