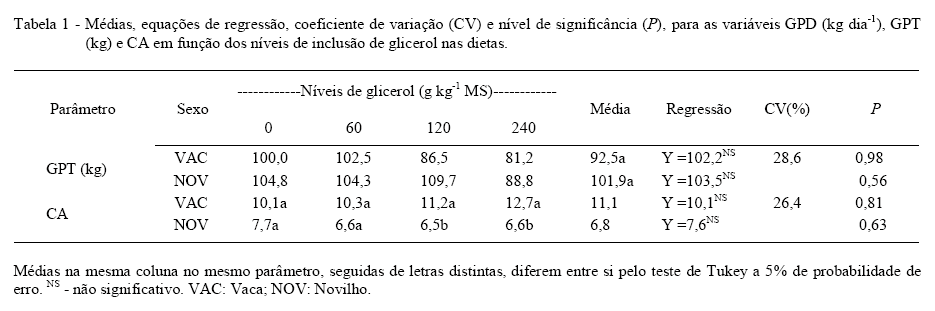
The increase in biodiesel production has led to higher production of crude glycerin, thus, numerous studies have highlighted the use of crude glycerin and glycerol as energy source to be used for animal feed production. However, its use has been closely watched because of the presence of contaminants such as methanol used in the process of separating fatty acids from glycerol. Methanol is an alcohol and has been responsible for intoxication in humans and primates, characterized by metabolic acidosis and eye problems, with less toxicity to other species. The toxic effects of methanol poisoning are attributed mainly to formic acid, a metabolite of the degradation process of methanol in the liver. The objective of this study was to verify the possible toxic action of crude glycerin and methanol by pathological examinations of the central nervous system (CNS), liver, rumen, small intestine and kidney from 24 feedlot cattle for 84 days, feed containing up to 24% of crude glycerin in dry matter (DM) presenting in its composition 80.35% glycerol, and <0.01% methanol. There were no pathological changes observed in dairy cows and steers up to 24% of glycerol inclusion based on the diet DM. The total weight gain and feed conversion were not affected by inclusion of glycerol. We conclude that crude glycerin can be included up to 24% of total DM in the diets of steers and dairy cows without compromising animal performance or display toxicity.
biodiesel; formic acid; glycerol; metabolic acidosis