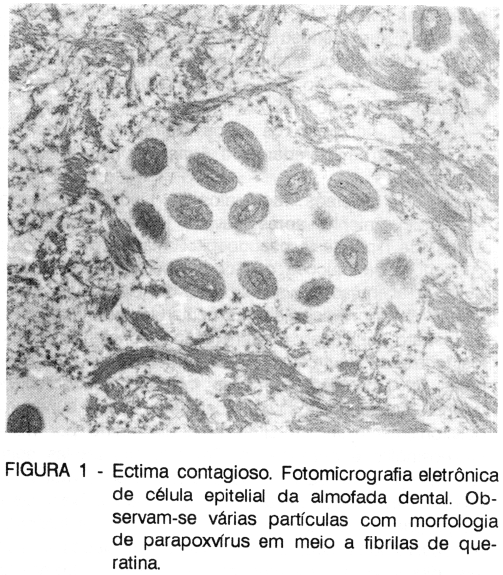
An outbreak of contagious ecthyma of sheep occuring in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil in June/July is described. Seventy (78%) out of 90 lambs 10 to 45-day-old were affected with no mortalities. Additionally 3 adult sheep developed mild lesions in the skin around the mouth. The lambs had nodular or plaque-like, firm, crustous proliferations in the skin of the mouth and mucocutaneous junctions of the oral cavity. Proliferative non ulcerated plaque-like lesions were observed on the hard palate and dental pad. Extensive, red, verrucous proliferations were seen in the gums of the upper and inferior molar teeth. One 45-day-old female lamb was killed and necropsied, Microscopically the main lesions consisted of hyperplastic, hyperkeratotic, and parakeratotic, ocasionally ulcerated, pseudoepitheliomatous ephitelia covering the dermis or lamina propia which were heavily infiltrated by macrophages, neutrophils and lymphocytes. Intracytoplasmic acidophilic inclusion bodies were seen in the epithelial cells of the skin and oral mucosa. Pustules were observed in the epidermis and oral mucosa. Vasculitis and associated thrombosis were observed in vessels of the dermis or lamina propria. Up on electron microscopy examination numerous viral particles with morphology compatible with parapoxvirus were found associated with the epithelial lesions. The epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and prophylaxis of contagious ecthyma are discussed.
ecthyma; viral diseases; poxviridae; sheep diseases