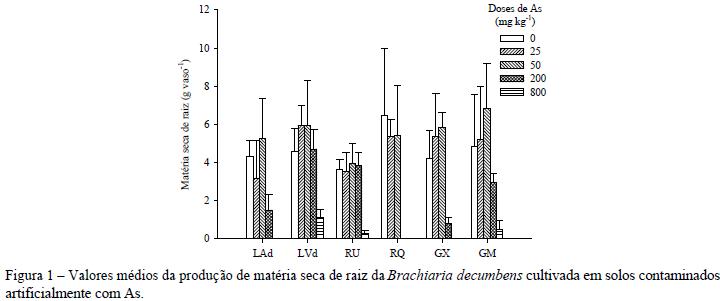
This work evaluated the phytoextraction potential of arsenic (As) by Brachiaria decumbens growing under greenhouse conditions in six soils: a Dystrophic Yellow Latosol (LAd), a Dystrophic Red Latosol (LVd), a Fluvic Neosol (RU), a Quartzenic Neosol (RQ), a Haplic Gleysol (GX), and a Melanic Gleysol (GM). Arsenic was added to the soils as sodium arsenate heptahydrate (Na2HAsO4.7H2O) at the following doses: 0, 25, 50, 200, and 800 mg kg-1. The plants were collected 55 days after planting for determination of shoot and root dry matter production. Arsenic shoot and root contents were evaluated after digestion according to the USEPA 3051A method, following analysis by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy. Plant development was differently affected by As in the six different soil classes. There was low translocation of As and consequently most of the As was detected in the roots of Brachiaria decumbens. Therefore, this species could be considered tolerant but not an accumulator of arsenic, thus being indicated for revegetation programs in As-polluted soils and sediments.
Phytoextraction; Brachiaria decumbens; environmental contamination