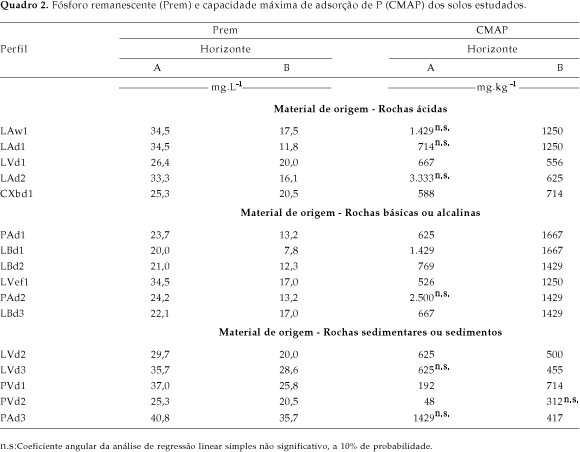
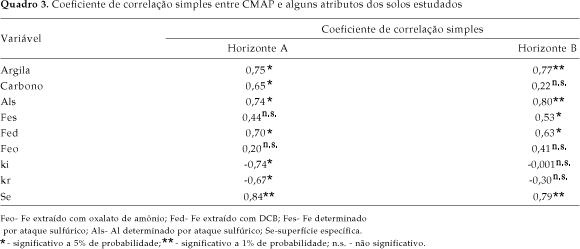
In this study possible correlations between physical and chemical properties and the maximum phosphorus adsorption capacity (MAPC) were evaluated in soils with low activity clay from different regions of Brazil, using samples from the surface (A) and subsurface (B) horizons of 16 soil profiles. The dosages for the determination of MAPC were calculated from the level of remaining phosphorus and they ranged from 0 to 135 mg L-1. From this data isotherms of P adsorption were built. Correlations were tested between MAPC and the clay content, organic carbon, ki, kr, specific surface, Al content determined by sulfuric acid attack, and content of different forms of extracted iron. A high variation in the values of MAPC for the surface horizon (48 to 1429 mg kg-1) and for the subsurface horizon (455 to 1667 mg kg-1) was observed. The correlation coefficients showed a significant association between MAPC and clay content, iron and aluminium determined by sulfuric acid attack and iron extracted by dithionite-citrate-bicarbonate (DCB). The multiple regression analysis showed a good fit to MAPC values based in soil attributes.
phosphate; tropical soils; Langmuir equation