Abstract
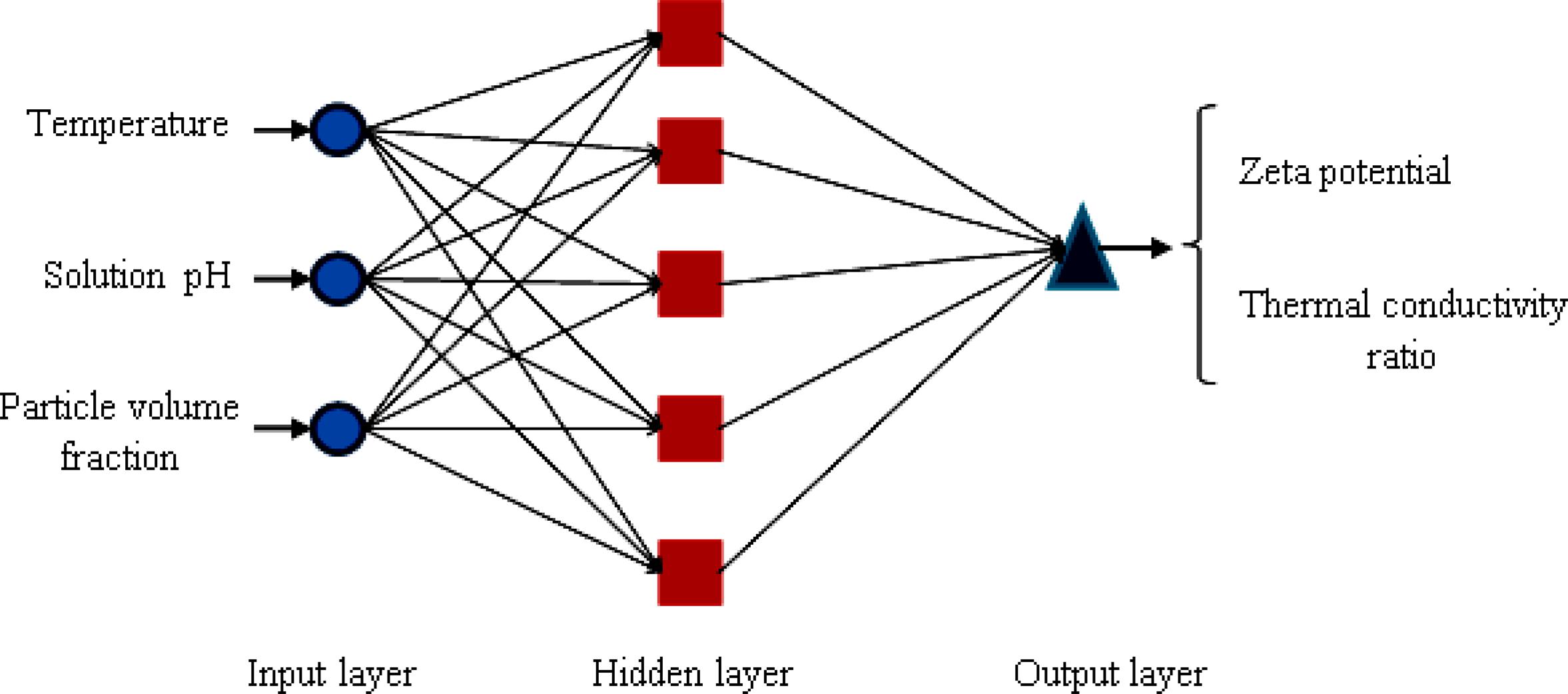
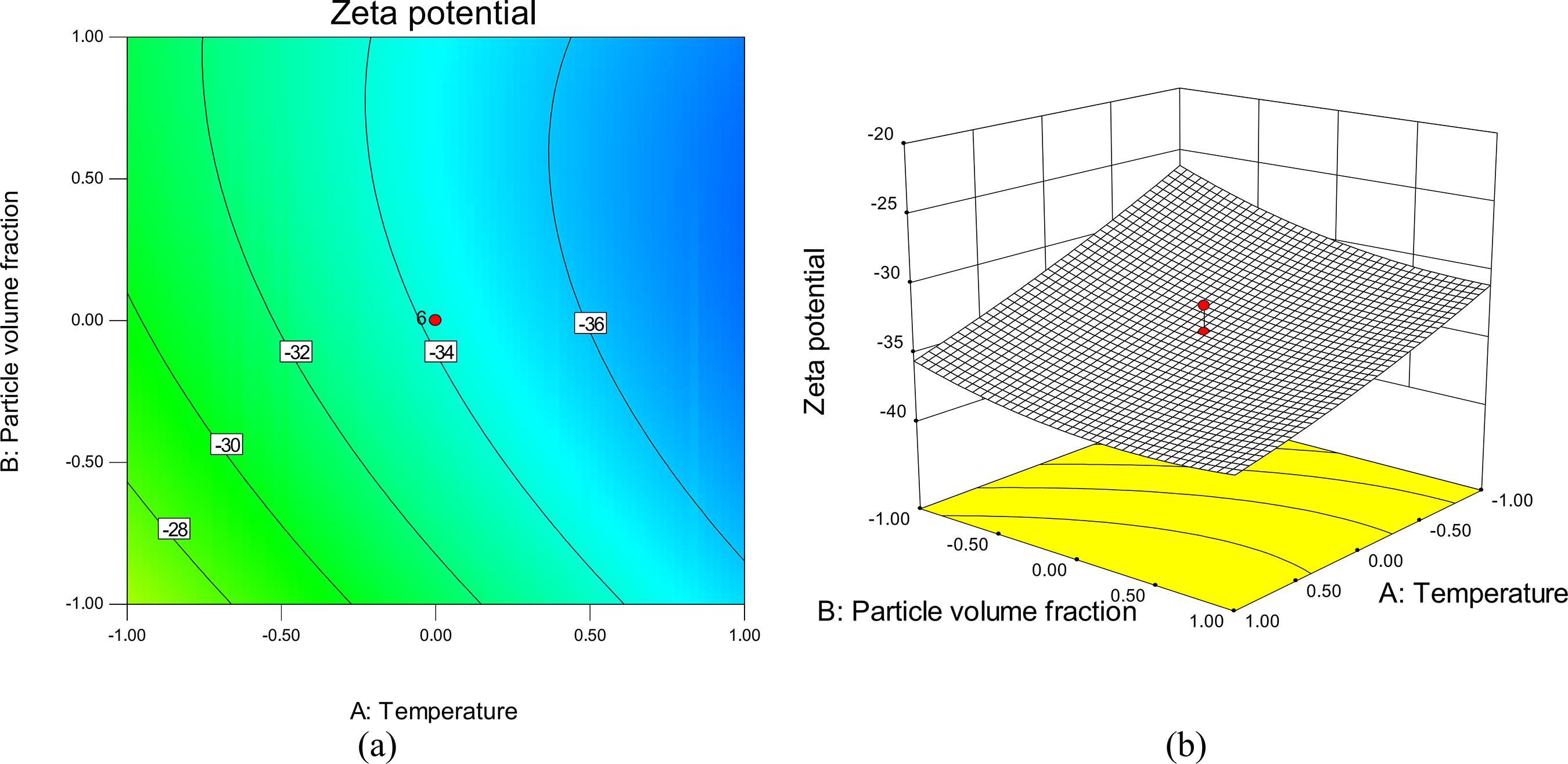
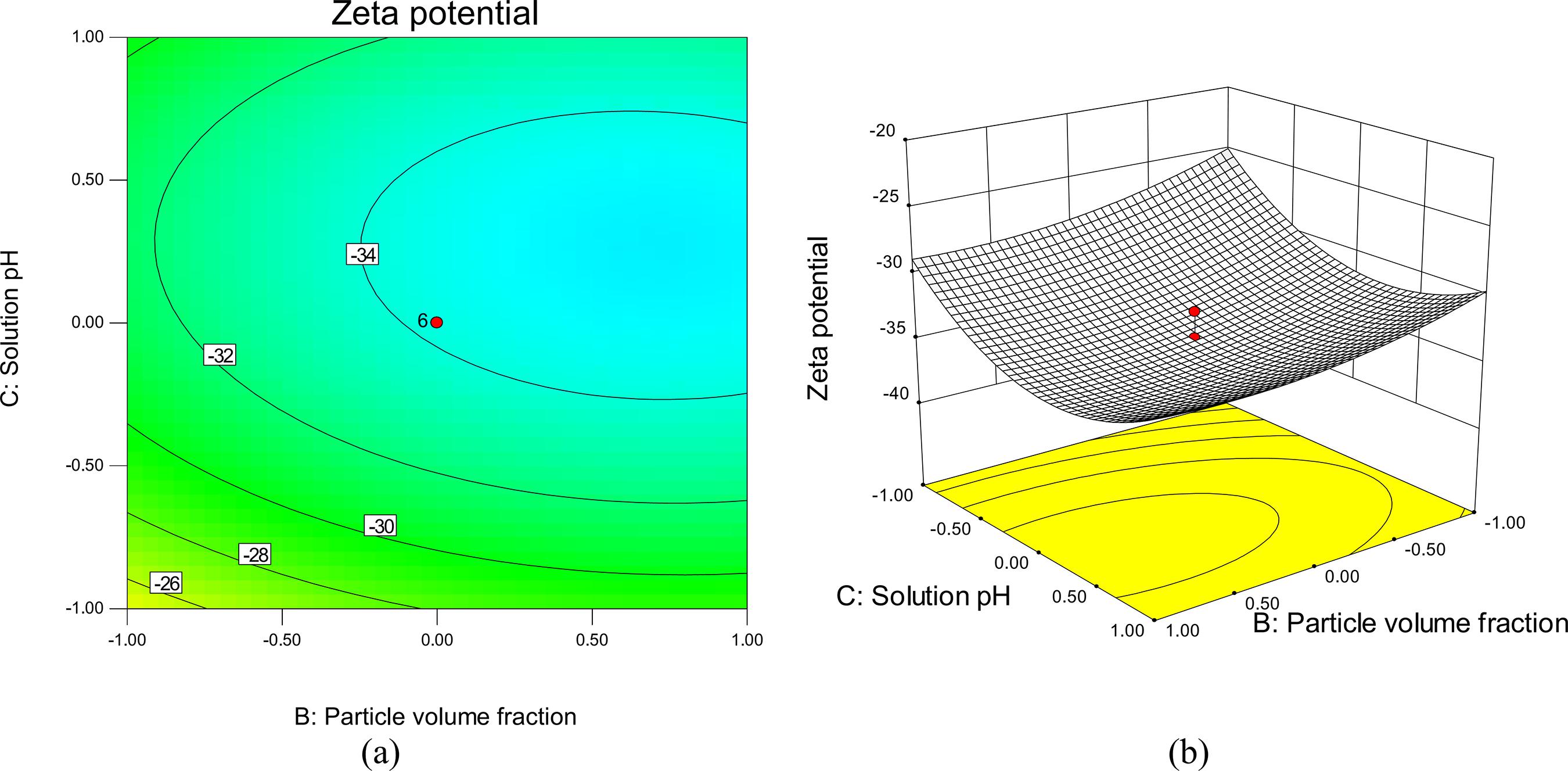
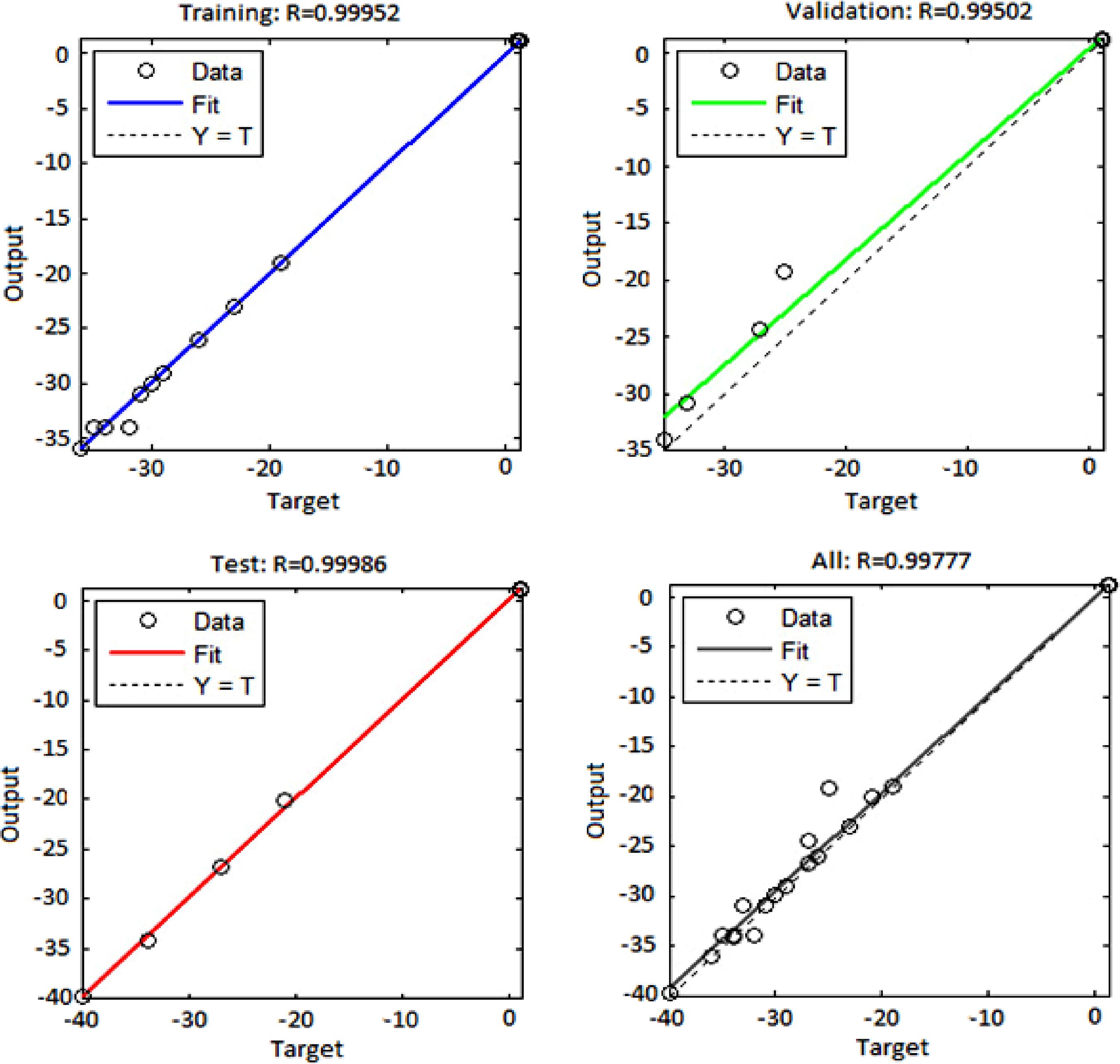
Central composite rotatable design (CCRD) and artificial neural networks (ANN) have been applied to optimize the performance of nanofluid systems. In this regard, the performance was evaluated by measuring the stability and thermal conductivity ratio based on the critical independent variables such as temperature, particle volume fraction and the pH of the solution. A total of 20 experiments were accomplished for the construction of second-order polynomial equations for both target outputs. All the influential factors, their mutual effects and their quadratic terms were statistically validated by analysis of variance (ANOVA). According to the results, the predicted values were in reasonable agreement with the experimental data as more than 96% and 95% of the variation could be predicted by the respective models for zeta potential and thermal conductivity ratio. Also, ANN proved to be a very promising method in comparison with CCD for the purpose of process simulation due to the complexity involved in generalization of the nanofluid system.
Keywords
Nanofluid; Central composite design; Artificial neural network; Statistical; Stability; Thermal conductivity