ABSTRACT
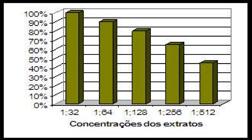
Buffaloes ranching presents illnesses similar to those of cattle, such as mastitis, causing losses for the producers, in regard to therapeutics. The improper antibiotic use of antibiotics increases the bacteria’s resistance, making it increasingly more difficult to treat mastitis, owing to the need to discover new effective compounds. The present study was aimed to evaluate the alternative control of mastitis with plants of the semi-arid region of Paraiba State, Brazil: jurema preta [Mimosa tenuiflora (Wild) Poiret] and neem (Azadiracta indica). The leaves of neem were collected on farms in the county of Patos, and the bark of jurema preta was collected from the farm of the Federal University of Campina Grande UFCG, Campus of Patos, with subsequent preparation of the ethanolic extract. The samples of Staphylococcus sp. were collected from milk of buffaloes with subclinical mastitis and sown in Petri plates containing agar-base complemented by 8% of defibrinated sheep blood. The plates were incubatedin a bacteriological chamber at 37º C, and the reading was carried out at 24 and 48 hs. The assays were carried out in duplicate, and the final result was determined by the arithmetic mean of halo inhibition. The ethanolic extract of jurema preta was efficient when compared with that of neem, on coagulasenegative Staphylococcus isolated from cases of subclinical mastitis in buffaloes.
KEY WORDS
Buffalo ranching; mastitis; treatment; Staphylococcus sp

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail


