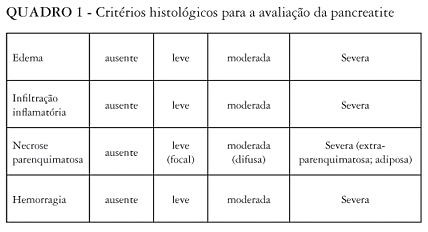
BACKGROUND: Excessive doses of basic amino acids such as L-arginine are able to injure the pancreas of rats. AIM: To describe and evaluate the biochemical and histological characteristics of acute pancreatitis in rats induced by L-arginine during the installation, development and repair stages of the pancreatic inflammatory process. MATERIAL AND METHODS - The study group consisted of 105 male Wistar rats. The rats in the experimental group (n = 70) received 500 mg/100 g of corporal weight L-arginine injection intraperitoneally. In the control group (n = 35), isotonic saline solution was injected. Ten rats in the experiment group and five in the control group were analyzed after 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hours, on the 7th and 14th days. During those times, blood samples were collected for laboratory testing and samples from the pancreas were collected for an optical microscopy analysis. RESULTS: From 12 to 24 hours after the injection of L-arginine, the amylase serum levels raised to their peak values when compared to the rats in the control group, decreasing gradually, reaching an equal level after the 48th hour and being significantly lower after 72 hours and 7 days. The enzymatic activity returned to its basal level after 14 days. The amylase values were normal in all the times evaluated in the control group. In optical microscopy, after the injection of L-arginine, a pancreatic architecture histologically preserved was observed after 6 hours, evidencing an important interstitial edema in 24 hours. After 48 hours, the acinar architecture was partially destroyed with focal cellular necrosis, reaching its maximum severity after 72 hours. On the 7th, the tissue necrosis and the edema had diminished, and the regeneration of the acinar architecture initiated. The pancreatic structural reconstruction could be observed after 14 days. Pancreatic histological changes were not found in the control group. CONCLUSION: - Experimental acute pancreatitis induced by L-arginine leads to pancreatic necrosis showing self-limited evolution with pancreas regeneration in 2 weeks.
Pancreatitis; Acute disease; Arginine; Rats