PURPOSE:
To compare the inflammatory reaction caused by the injection of a sugarcane biopolymer (SCB) into the vocal fold of rabbits with that caused by calcium hydroxyapatite (CaH).
METHODS:
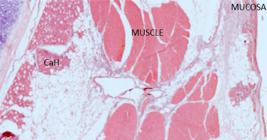
CaH (Radiesse(r)) and SCB gel were injected respectively into the right and left vocal cords of thirty rabbits. The rabbits were distributed into two equal groups and sacrificed at three and twelve weeks after injection. We then evaluated the intensity of the inflammatory reaction, plus levels of neovascularization, fibrogenesis and inflammatory changes in the vocal mucosa.
RESULTS:
The vocal cords injected with CaH had a stronger inflammatory reaction by giant cells in both study periods. The SCB group had a more intense inflammatory involvement of polymorphonuclear cells three weeks after injection. SCB caused a higher level of neovascularization compared with CaH three weeks after the procedure.
CONCLUSION:
Whereas calcium hydroxyapatite triggers a more intense and lasting inflammatory reaction mediated by giant cells, sugarcane biopolymer causes a greater response from polymorphonuclear leukocytes, as well as higher levels of vneoascularization three weeks after injection.
Vocal Cords; Dysphonia; Laryngoplasty; Biopolymers; Hydroxyapatites; Rabbits

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail





