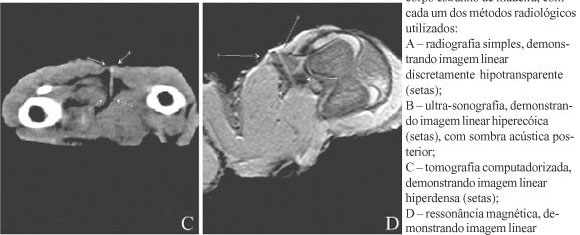
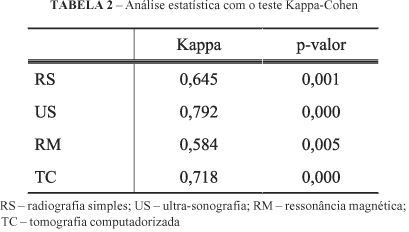
PURPOSE: To determine the usefulness of different radiological methods in the diagnoses of wooden foreign bodies (FB). METHODS: Eleven adult chickens were used. Each thigh received a puncture wound and in one of them a wooden splinter was introduced and left in place while in the contralateral it was introduced and removed (control group). After 7 days the animals where killed and the legs removed to be analyzed with conventional radiography (CR), ultrasonography (US), magnetic resonance and computed tomography. The results were viewed by 2 independent senior radiologists. RESULTS: Sensitivity was: CR - 13.6%; US - 63.6%; MR - 59.1%; and CT - 72.7%, with specificity of 100%, 100%, 95.5%, and 95.5%, respectively. The positive predictive value for CR and US was 100%, 95% for CT 95% and 93.8% for MR. CT had a negative predictive value of 78.3%, while US, MR, and CR had 73.7%, 70.1%, and 53.7%, respectively. The accuracy for CT was 84.1%, followed by US - 81.8%, RM - 77.3%, and CR - 56.8%. Inflammatory reaction was histologically demonstrated in all thighs containing FB. CONCLUSION: CR showed a poor performance to detect wooden FB in chickens, while US and CT seem to be the best option, followed by RM.
Foreign body; radiography; ultrasonography; magnetic resonance; computed tomography