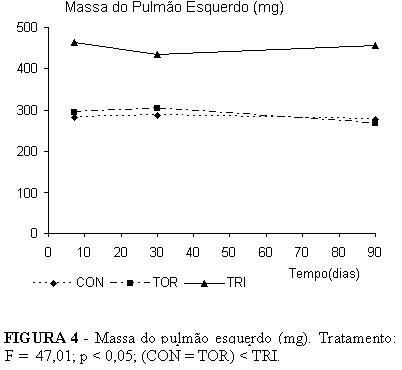
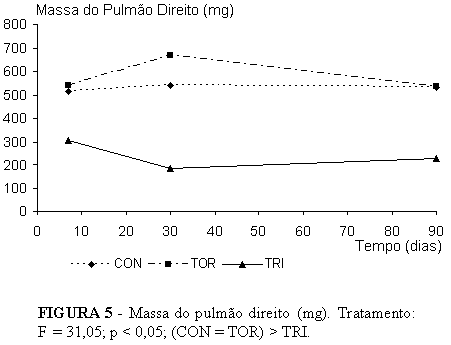
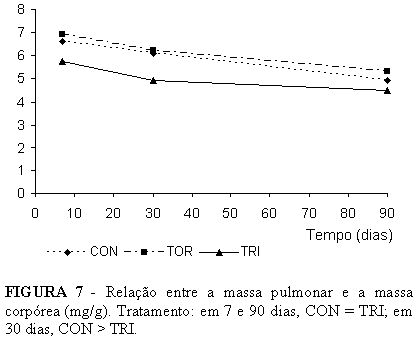
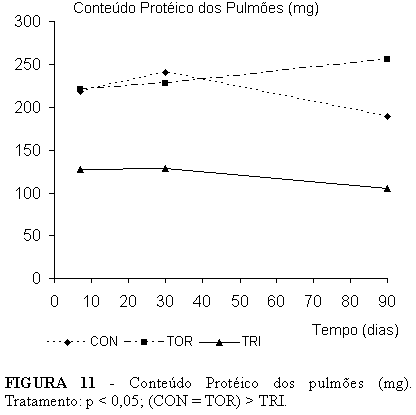
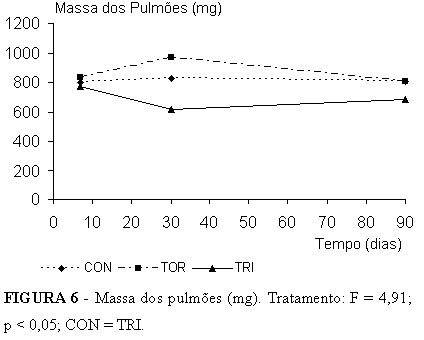PURPOSE: To evaluate the biochemical behavior of compensatory lung growth after trilobectomy in undernourished rats. METHODS: Undernutrition was achieved by offering 33% normal daily diet to 137 adult male Wistar rats over an acclimatization period and throughout the experiment. Rats were randomly distributed into nine (3 Control, 3 Thoracotomy, and 3 Trilobectomy) groups. Analysis was 7, 30, and 90 days after surgery (Trilobectomy is middle, accessory and caudal lobectomies). Body mass, lung mass, and lung tissue protein content were studied. RESULTS: Cranial lobe and left lung mass both larger in trilobectomized rats throughout the study compared to the other groups. Comparing combined lung mass, we noted that there was sufficient compensatory growth to be on a par with controls. Cranial lobe and left lung protein content in trilobectomized rats both displayed the same behavior as lung mass throughout the study, but the compensatory growth in the remaining two lobes was not sufficient to make up for trilobectomy losses. CONCLUSION: In adult undernourished rats, there was compensatory lung growth after trilobectomy, there was also lung mass recovery at the beginning of the study compared to other groups. Throughout the study, cranial lobe and left lung protein content were higher in trilobectomized rats than other groups.
Lung; Nutricion disorders; Wistar rats