Abstract
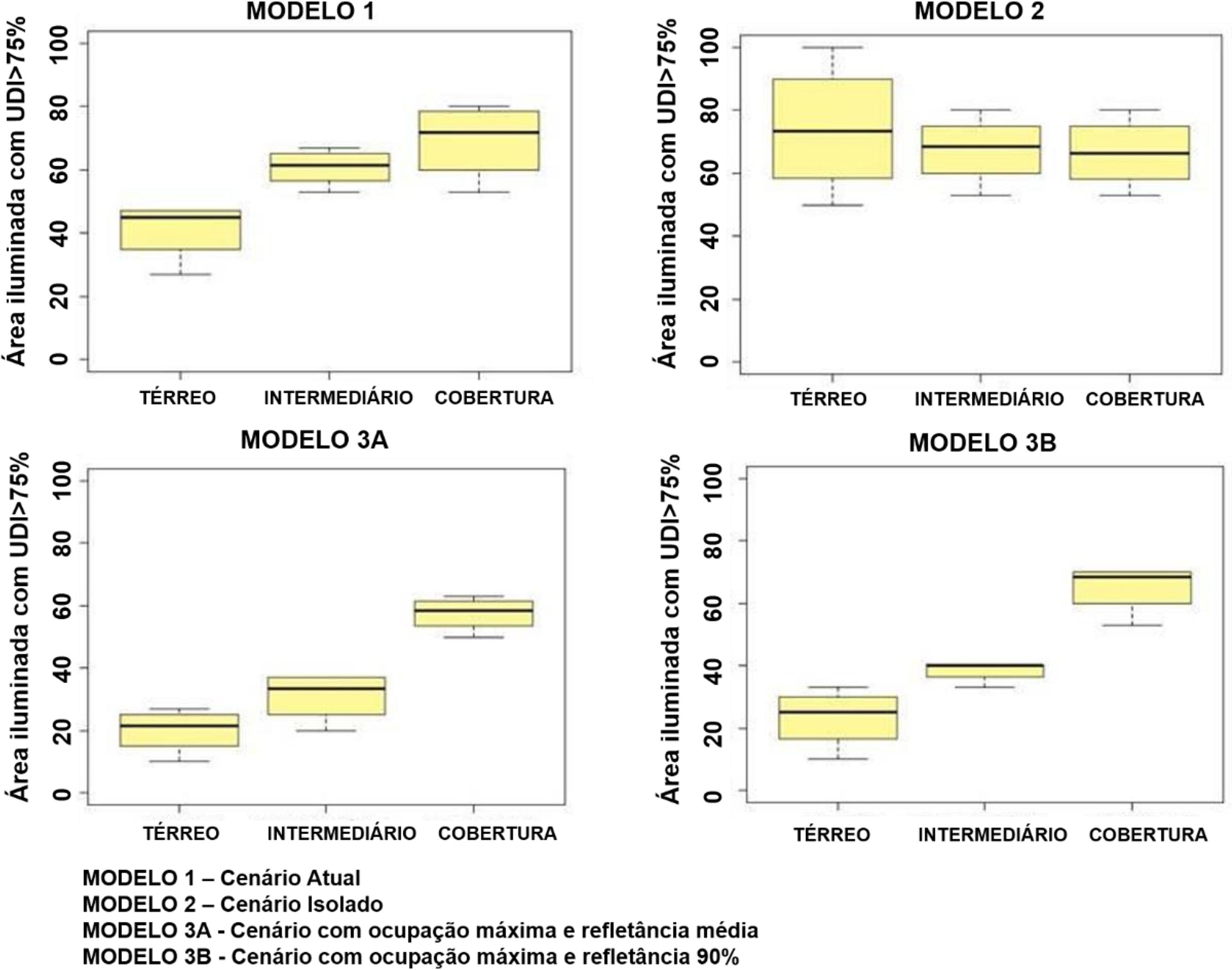
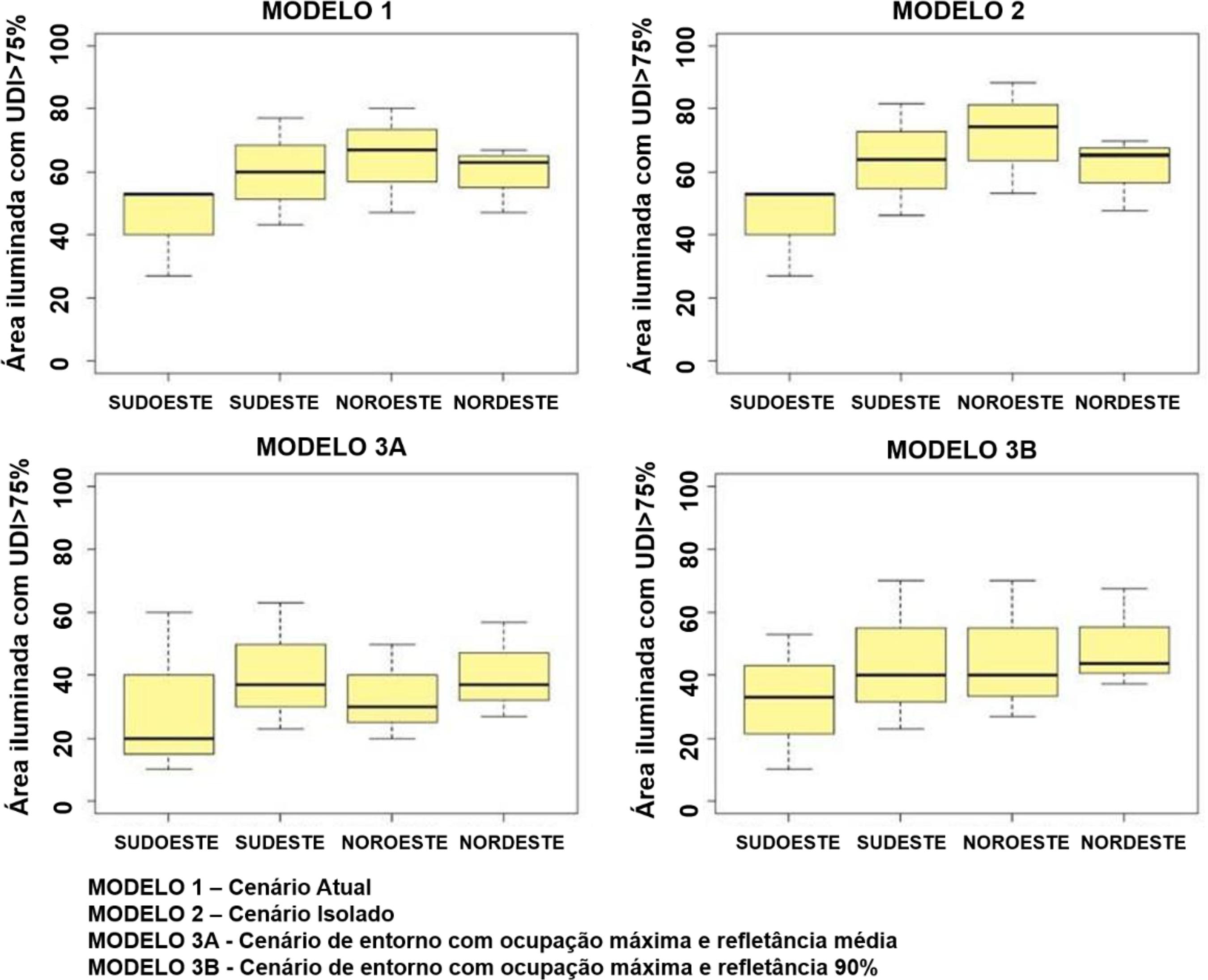
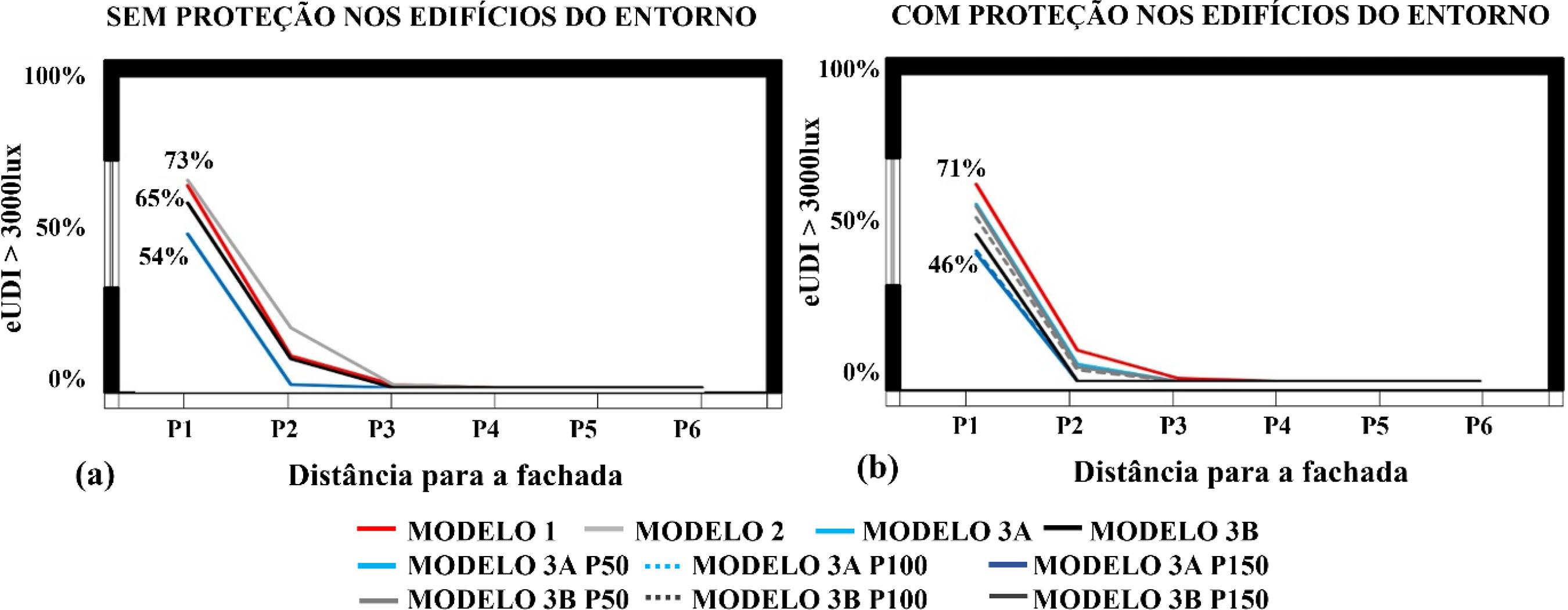
The aim of this study is to investigate sky obstruction in the urban fabric and its impact on daylighting and glare. Rooms in a multi-storey residential building were analysed using data from a hot and humid climate. The daylighting performance and glare levels inside the analysed rooms were accessed through climate-based simulations, using Daysim and Evalglare. A total of 120 room variations were studied, resulting from the combination of the following variables: (a) urban fabric scenarios, (b) reflection coefficient on the buildings, (c) horizontal sun shading on neighbouring facades and windows, d) floor height, and finally e) geographic orientation. The daylighting and glare performance parameters used were: useful illuminance (UDI), excessive illuminance (eUDI) and daylight glare probability (DGP). The main results highlighted in this study are: (a) a reduction of aUDI by 21.5% with the maximum obstruction scenario and by 40% in rooms located on the ground floor; (b) a higher reflection coefficient increased the illuminated area by 8.5%, with less effect on the ground floor, at only 3%; (c) a lower probability of glare was observed with higher sky obstruction; d) reduction of excessive illuminance and glare with the shading caused by the insertion of horizontal sun shading on neighbouring facades; (e) glare chance and a high reflection coefficient on the buildings are directly proportional variables.
Keywords:
Daylighting; Glare; Computer simulation

 Fonte: adaptada do
Fonte: adaptada do  Fonte: adaptada d e
Fonte: adaptada d e