Abstract
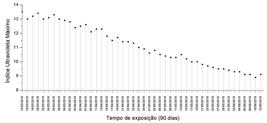
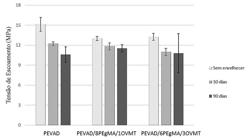
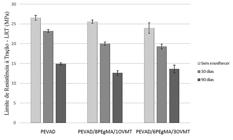
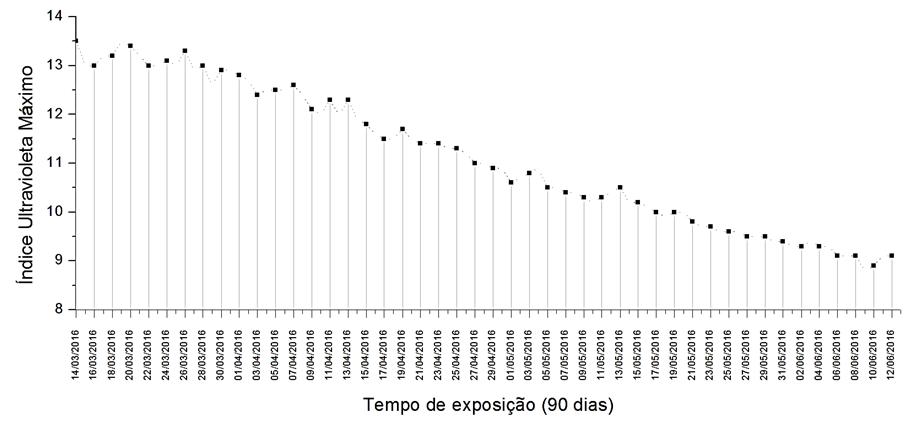
Green polyethylene and vermiculite clay composites were developed through the fusion intercalation technique with the aim of investigating their potential use as a building material. The composites were processed in a single screw extruder and molded in a hydraulic thermopress. For the purpose of this study, flame propagation resistance and the natural aging effects of green polyethylene and its composites were analyzed. The samples were exposed to the abiotic degradation test for 90 days with the aim of assessing the effects of climate conditions on the material’s morphology and mechanical properties. The flammability test demonstrated the catalytic effect of the clay, since for all composites evaluated, the flame propagation resistance was inferior to that of the pure green polymer. The effects of natural aging on the morphology of the materials were characterized by the transition of the polymeric matrix from a ductile aspect to a more fragile appearance and the emergence of voids and internal fractures Hence, the mechanical performance of the systems was directly affected, as a result of several types of abiotic degradation suffered by the samples.
Keywords:
Green polyethylene; Vermiculite clay; Polymer composites; Flame propagation; Weathering; Building material

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail




 Fonte:
Fonte: 


