Abstract
The world’s demand for energy is constantly increasing,while, at the same time, the reserves of fossil fuels are decreasing and will not be enough to satisfy the global energy demand in the future. In addition, conventional heating and cooling systems consume most of the energy demand and considerably increase costs. Earth-airheat exchangers (EAHE) are a sustainable option that consumes less energy and has the potential to improve thermal conditions in buildings. Despite it being a simple and old technology, research into this type of technology is verylimited in Brazil. There is a lack of studies in the northern region of this country, particularly in the city of Belém do Pará. Hence, the goal of this researchstudy was to develop a three-dimensional numerical model of EAHE using ANSYS Fluent to evaluate the influence of operational and constructive parameters such as air flow velocity, length and diameter of the duct on the thermal performance of this system adapted to climatic conditions and soil characteristics of this city. The results obtainedlead to the conclusionthat this system can reduce the air temperature at the duct outlet up to 5.91 °C.
Keywords:
Earth-Air Heat Exchangers (EAHE); Building cooling; Numerical simulation; Renewable energy

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
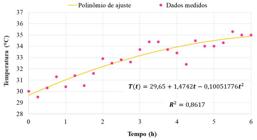 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
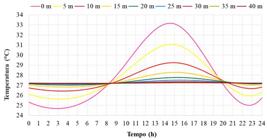 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
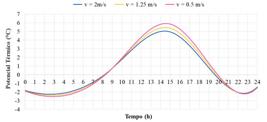 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
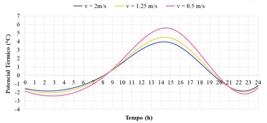 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
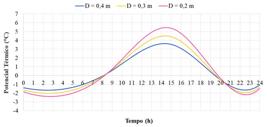 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail





 Fonte: Laboratório de Eficiência Energética em Edificações (2019).
Fonte: Laboratório de Eficiência Energética em Edificações (2019).
 Fonte: European Centre for Medium-Range WeatherForecasts (2019).
Fonte: European Centre for Medium-Range WeatherForecasts (2019).


 Fonte: adaptado de
Fonte: adaptado de 
 Fonte:
Fonte: 








