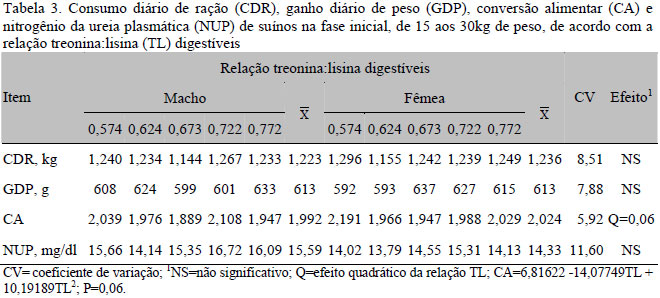
Two experiments were carried out to evaluate the effect of digestible threonine:lysine ratio (TL) on nitrogen (N) use and on growth performance of starting pigs (15-30kg). Experiment I evaluated nitrogen balance using twenty high-lean commercial crossbred barrows, with initial weight of 23.0±4.1kg. Pigs were allotted in a randomized design. Diets were formulated with low crude protein levels (17.3 %) and TL ratios were: 0.574; 0.624; 0.673; 0.722; and 0.772. Excreted crude protein (CPEX), crude protein retention (CPR), and net protein utilization (NPU) showed quadratic effect and the best TL ratio values were achieved at 0.648, 0.648, and 0.649, respectively. The best TL ratio was 0.649 (CPR and NPU means). Experiment II was carried out to examine the same TL ratio effects on the performance of pigs. Sixty pigs (30 barrows and 30 gilts), averaging 15.5±1.5kg, used in experiment II, were allotted in a randomized design, following a factorial scheme (5x2), being five TL ratios (same as in experiment I) and two genders. Six pens per treatment (three barrows and three gilts) were used. There was no effect of TL ratio on daily feed intake and on average weight gain. However, the feed:gain ratio showed a quadratic effect and the best TL ratio was achieved at 0.691. The results pointed out that the 0.649 TL ratio maximized nitrogen retention and the 0.694 TL ratio allowed a better feed conversion for starting pigs averaging 15 to 30kg of b.w.
starting pig; aminoacid; nitrogen balance; ideal protein; performance