ABSTRACT
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of diets with different energy levels on nutrient intake, milk production and composition, body weight and benefit:cost ratio of a dairy goat production. Nine goats were distributed in a triple 3 x 3 latin square design. The experiment lasted for 60 days, divided into three 20-day periods. Complete rations containing three energy levels were evaluated: 65%, 70% and 75% of TDN. The dry matter intake, crude protein and mineral matter consumption were higher (P <0.05) in the diets with higher levels of energy compared to the diet with 65% of TDN. Milk production was similar (P> 0.05) in goats receiving diets containing 70% and 75% TDN, but these diets produced more milk (P<0.05) than the diet with 65% of TDN. The diet with 75% of TDN allowed a higher (P<0.05) final body weight (P<0.05) when compared to diets containing 65% and 70% TDN. There was no difference (P> 0.05) in the physical-chemical parameters of fat, lactose, crude protein, defatted dry extract, density, salts and conductivity of the milk. Therefore, goats fed with diets of 70% and 75% of TDN in the total diet increased milk production. However, the diet with 75% of TDN provides a better benefit:cost ratio, as for every $ 1.00 in the cost invested, there was $ 1.52 of financial return.
Keywords:
dairy goat; does; nutrition; productivity

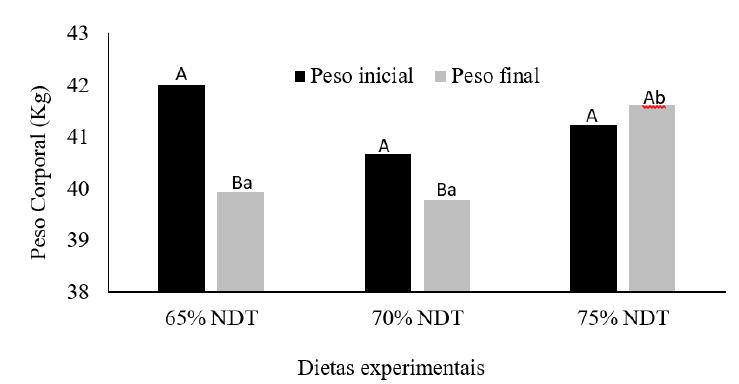 Letras maiúsculas (A, B) indicam diferenças (P<0,05) no peso corporal dentro do mesmo nível de NDT. Letras minúsculas (a, b) indicam diferenças no peso corporal final (P<0,05) entre os diferentes níveis de NDT.
Letras maiúsculas (A, B) indicam diferenças (P<0,05) no peso corporal dentro do mesmo nível de NDT. Letras minúsculas (a, b) indicam diferenças no peso corporal final (P<0,05) entre os diferentes níveis de NDT.