Abstract
A proteína Kint3-4 (PKint3-4), codificadora da angiostatina, é reconhecida por sua potencialidade antiangiogênica. O presente estudo teve como objetivo avaliar o efeito da proteína Kint3-4 no crescimento do tumor sólido de Ehrlich. Para isso, foram analisados a curva de desenvolvimento tumoral, o índice apoptótico e a dosagem de hemoglobina, a fim de se avaliar a angiogênese, em 20 camundongos Swiss fêmeas, inoculadas com o tumor sólido de Ehrlich em seus coxins plantares. Os resultados demonstraram a participação de PKint3-4 na indução à apoptose de células neoplásicas, na diminuição da concentração de hemoglobina e, principalmente, na diminuição do desenvolvimento tumoral. Sugere-se que a ação antitumoral, determinada pela sequência proteica utilizada, possa estar associada ao papel antiangiogênico da angiostatina, que indiretamente aumentaria o índice apoptótico das células neoplásicas, e/ou a uma ação direta da proteína Kint3-4 sobre essas células, estimulando-as a sofrerem apoptose.
camundongo; tumor de Ehrlich; Kint3-4; apoptose; angiogênese; caspase-3; tumor de Ehrlich; mice; Ehrlich tumor; Kint3-4; apoptosis; angiogenesis; caspase-3
camundongo; tumor de Ehrlich; Kint3-4; apoptose; angiogênese; caspase-3; tumor de Ehrlich; mice; Ehrlich tumor; Kint3-4; apoptosis; angiogenesis; caspase-3
COMMUNICATION COMUNICAÇÃO
Kint3-4 promotes apoptosis and inhibition of angiogenesis in solid Ehrlich Tumor
Kint3-4 promove apoptose e inibição da angiogênese no tumor sólido de Ehrlich
C. Souza1; L.F. CarvalhoI; M.A.N.D. FerreiraI,II; J.L. PesqueroII; G.D. CassaliI,* * Autor para correspondência ( corresponding author) E-mail: cassalig@icb.ufmg.br
Instituto de Ciências Biológicas - Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais - Belo Horizonte, MG
RESUMO
A proteína Kint3-4 (PKint3-4), codificadora da angiostatina, é reconhecida por sua potencialidade antiangiogênica. O presente estudo teve como objetivo avaliar o efeito da proteína Kint3-4 no crescimento do tumor sólido de Ehrlich. Para isso, foram analisados a curva de desenvolvimento tumoral, o índice apoptótico e a dosagem de hemoglobina, a fim de se avaliar a angiogênese, em 20 camundongos Swiss fêmeas, inoculadas com o tumor sólido de Ehrlich em seus coxins plantares. Os resultados demonstraram a participação de PKint3-4 na indução à apoptose de células neoplásicas, na diminuição da concentração de hemoglobina e, principalmente, na diminuição do desenvolvimento tumoral. Sugere-se que a ação antitumoral, determinada pela sequência proteica utilizada, possa estar associada ao papel antiangiogênico da angiostatina, que indiretamente aumentaria o índice apoptótico das células neoplásicas, e/ou a uma ação direta da proteína Kint3-4 sobre essas células, estimulando-as a sofrerem apoptose.
Palavras-chaves: camundongo, tumor de Ehrlich, Kint3-4, apoptose, angiogênese, caspase-3, tumor de Ehrlich
Keywords: mice, Ehrlich tumor, Kint3-4, apoptosis, angiogenesis, caspase-3
Among the several endogenous inhibitors of angiogenesis, the angiostatin has been the target of related research to the antineoplastic tretaments (Tabruyn and Griffioen., 2007; Hayashi et al.,2008). Recently, a recombinant glycosylated Kint3-4 protein (PKint3-4), derived from angiostatin, demonstrated antiinflammatory and antiangiogenic action in tumor and sponge models. . This protein was expressed in P. pastoris. It has the aminoacids Val79-Thr346, three glycosylation sites corresponding to the K1-3 fragment of human plasminogen and fusion between Val79 and eight amino acids (EAEAYVEF) from peptide AOX1 (Santos et al., 2010; Souza et al., 2011).
The antiangiogenic effects of the angiostatin derivatives are extensively demonstrated in different anti-tumor studies (Galaup et al., 2005; Yang et al., 2005; Schmitz et al., 2007). However, most studies do not elucidate the effects on the tumor cells themselves, as apoptosis, which has an important action in determining the tumor growth and its aggressiveness (Cao et al., 1999; González- Cámpora et al., 2000). This study aimed to evaluate the effect of Kint3-4 protein in the growth of solid Ehrlich tumor from the analysis of angiogenic activity and the apoptotic index.
All procedures performed in this work were approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Experimentation (CETEA/UFMG under protocol number 44/06). The solid Ehrlich tumor was obtained inoculating 50μL of solution containing 2.5x106 neoplastic cells of ascitic Ehrlic tumor between the plantar cushions of the left posterior hind limb (Dagli et al., 1989). Twenty female Swiss mice with 45 days old were used. These animals were divided into two groups of ten animals. Treated group received intraperitoneally 4.5µg/300µL/animal of the Kint3-4 protein at intervals of 48 hours during ten consecutive days. The control animals received saline by the same way and in the same period. The tumor development curve was made from the measurement of the paw of the animals using micrometer (Mitutoyo, measurement 0.01mm, series number 7301). The animals were euthanized after the last treatment and tumor fragments were obtained, which were fixed in formalin (10% w/v in phosphate-buffered saline PBS pH 7.4), processed and embedded in paraffin for immunohistochemical analysis.
Assessment of apoptosis was performed using histological sections of 4μm. It was used the streptavidin-biotin-peroxidase technique (Ultra Vision Large Volume Detection System Anti- Polyvalent, HRP ready to use Lab Vision), and antigenic recovery was made in wet heat with citrate buffer pH 6.0 during 20 minutes. The apoptotic cells were marked using the antibody against caspase-3 (clone Ab4) at a dilution of 1:300 (Neomarkes Laboratories). The slides were incubated in a moist chamber for 1h with primary antibody and for 15min in the steps of blocking endogenous peroxidase, blocking serum (Ultra Vision Block, Lab Vision), second antibody (Biotin Goat, Lab Vision) and streptavidin peroxidase (Streptavidin Peroxidase, Lab Vision). The chromogen used was DAB (diaminobenzidina DAB Substrate System, Lab Vision) incubated for 10 minutes. The sections were counter-stained with Harris's hematoxylin. The count of apoptotic cells was analyzed in 500 tumor cells in 15 fields of each slide with 40x objective, considering the marking with caspase-3 and the following characteristics of the apoptotic cells: shrinkage and loss of cell adherence, cytoplasm and nucleus condensation and formation of apoptotic bodies (Kerr et al., 1972).
The evaluation of angiogenesis was performed using other tumor fragment to hemoglobin dosage (Hb). This technique is considered a well established estimation of vascular index in tissues and it has been proposed as an useful tool in studies of experimental oncology (Belo et al., 2004; Ferreira et al., 2007). In this study, the absorbance was read at 540nm and the results were expressed in mgHb/mg tissue.
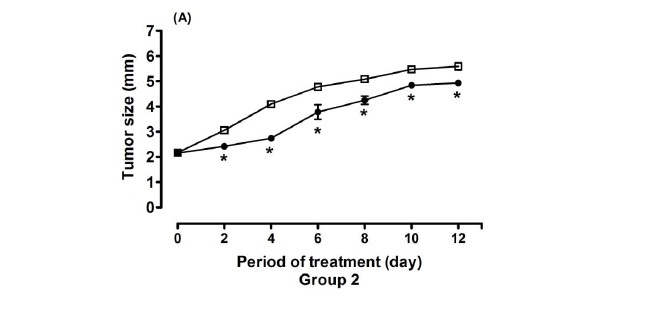
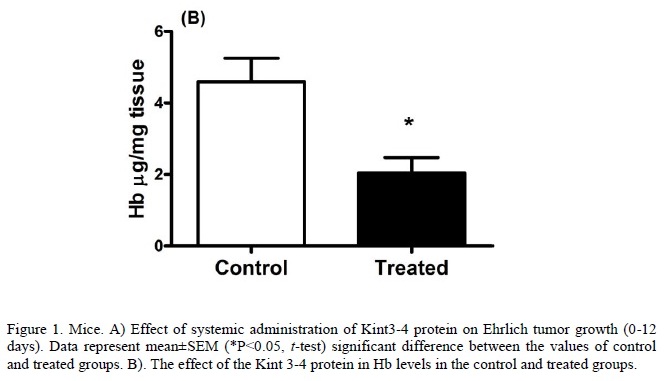
In the analyses of tumor growth curve (Figure 1A), it is observed that significant differences between control and treated groups were already present on the second day after inoculation. Tumor growth in the treated group was significantly lower, and remained in the subsequent days of analyses (P<0.05). In the hemoglobin dosage (Figure 1B), it was observed that the Hb concentration in the treated group (2.11±0.96) was significantly lower than in the control group (3.33±0.87), P<0.05.
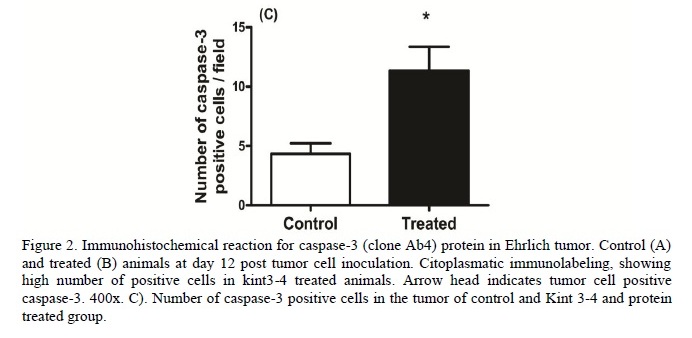
The present results demonstrated that in animals treated with Kint3-4 there was a greater express1on of caspase-3 in neoplastic cells (P<0.05) (Figure 2A-C). Animals treated with the Kint3-4 protein had a lower tumor development. The results suggest that the anti tumor action, determined by protein sequence, may be linked to anti-angiogenic role of angiostatin.
Other studies describe the antiangiogenic action of angiostatin which was determined mainly by controlling the migration and proliferation of endothelial cells and induction of apoptosis in these cells (Benelli et al., 2002; Moulton et al., 2003). Thus, the reduction of angiogenesis could indirectly lead to increased apoptotic index of neoplastic cells.
Apart from these well acknowledged angiostatic effects, some studies furthermore indicate direct cytopathic effects on neoplastic cells inducing apoptosis and this way contributing to the decrease of cell proliferation in certain tumors (Schmitz et al., 2002; Magnon et al., 2005; Yang et al., 2005). Nevertheless, the occurrence of anti-tumor effects is not a common phenomenon and depends on the tumor type (Magnon et al., 2005; Raskopf et al., 2005).
The present study demonstrated that treatment with Pkint3-4 leads to decreased angiogenesis, increased apoptosis and, consequently, reduced the development of Ehrlich tumor. However, it is not clear whether there is a direct effect of this derivative of the angiostatin on tumor cells, causing them to undergo apoptosis and decreasing their proliferation or this is due to only the antiangiogenic effect. Future studies related to the action of the protein Kint3-4 about the morphological and molecular behaviors of the tumor development will enable a better understanding of its mechanism of action in angiogenesis and on tumor cells, directing to new applications in anti-cancer treatments.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Recebido em 1 de dezembro de 2011
Aceito em 8 de fevereiro de 2012
- BELO, A.V.; BARCELOS, L.S.; FERREIRA, M.A.N.D. et al. Inhibition of inflammatory angiogenesis by distant subcutaneous tumor in mice. Life Sci., v.74, p.2827-2837, 2004.
- BENELLI, R.; MORINI, M.; CARROZZINO, F. et al. Neutrophils as a key cellular target for angiostatin: implications for regulation of angiogenesis and inflammation. FASEB, v.16, p.267-269, 2002.
- CAO, R.; WU, H.L.; VEITONMAKI, N. et al Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by the inhibitor K1-5 generated by plasmin-mediated proteolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., v.96, p.5728-5733, 1999.
- DAGLI; M.L. Disseminação linfática do tumor de Ehrlich: Estudo experimental. 1989. 148f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Patologia Experimental e Comparada) - Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo.
- FERREIRA, M.A.N.D.; BARCELOS, L.S.; TEIXEIRA M.M. et al. Tumor growth, angiogenesis and inflammation in mice lacking receptors for platelet activating factor (PAF). Life Sci., v.81, p.210-217, 2007.
- GALAUP, A.; MAGNON, C.; ROUFFIAC, V. et al. Full kringles of plasminogen (aa 1-566) mediate complete regression of human MDA-MB-231 breast tumor xenografted in nude mice. Gene Ther., v.10, p.831-842, 2005.
- GONZÁLEZ-CÁMPORA, R.; GALERA, R.M.R.; VÁZQUEZ, R.F. et al Apoptosis in breast carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract., v.196, p.167-174, 2000.
- HAYASHI, M.; TAMURA, Y.; DOHMAE, N. et al Plasminogen N-terminal activation peptide modulates the activity of angiostatin-related peptides on endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Bioch. Bioph. Res. Commun., v.1, p.1-6, 2008.
- KERR, N.F.; WYLLIE, A.H.; CURRIE, A.R. Apoptosis: a base biological phenomenon with wide- ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer, v.26, p.239-257, 1972.
- MAGNON, C.; GALAUP, A.; MULLAN, B. et al. Canstatin acts on endothelial and tumor cells via mitochondrial damage initiated through interaction with alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5 integrins. Cancer Res., v.65, p.4353-61, 2005.
- MOULTON, K.S.; VAKILI, K.; ZURAKOWSKI, D. et al. Inhibition of plaque neovascularization reduces macrophage accumulation and progression of advanced atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., v.100, p.4736-4741, 2003.
- RASKOPF, E.; DZIENISOWICZ, C.; HILBERT, T. et al Effective angiostatic treatment in a murine metastatic and orthotopic hepatoma model. Hepatology, v.41, p.1233-1240, 2005.
- SANTOS, I.C.; SILBIGER, V.N.; HIGUCHI, D.A. et al Angiostatic activity of human plasminogen fragments is highly dependent on glycosylation. Cancer Sci., v.101, p.453-459, 2010.
- SCHMITZ, V.; RASKOPF, E.; GONZALEZ- CARMONA, M.A. et al. Plasminogen fragment K1-5 improves survival in a murine hepatocellular carcinoma model. Gut, v.56, p.271-278, 2007.
- SCHMITZ, V.; WANG, L.; BARAJAS, M. et al A novel strategy for the generation of angiostatic kringle regions from a precursor derived from plasminogen. Gene Ther., v.23, p.1600-1606, 2002.
- SOUZA, C.M.; FERREIRA, E.; FERREIRA, M.A.N.D. et al. Kint3-4 protein from human plasminogen delays Ehrlich tumor growth in mice. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab., v.47, p.465-472, 2011.
- TABRUYN, S.P.; GRIFFIOEN, A.W. Molecular pathways of angiogenesis inhibition. Bioch. Bioph. Res. Commun., v.355, p.1-5, 2007.
- YANG, D.Z.; HE, J.; ZHANG, J.C. et al. Angiostatin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and growth in nude mice. World J. Gastroenterol., v.11, p.4992-4996, 2005.
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
02 July 2012 -
Date of issue
June 2012
History
-
Received
01 Dec 2011 -
Accepted
08 Feb 2012