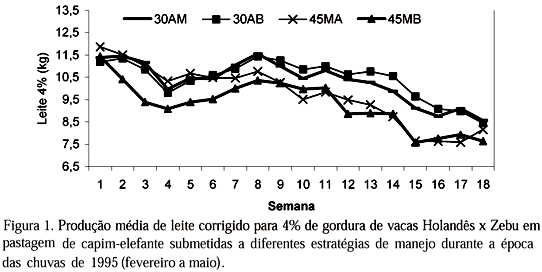
The objective of this trial was to study the effect of different strategies of grazing management on milk production of cows on elephantgrass pastures. The treatments were: 30 days of grazing interval (GI) and fertilized monthly (30MF); 30 days GI and fertilized every two months (30BM); 45 days GI and a stubble height of 90-100cm (45HS); 45 days GI and a stubble height of 40-50cm (45LS). In treatments 30MF and 30BM the stubble height was 90-100cm. Each paddock was grazed for three days. Twenty four Holstein × Zebu cows were allocated to treatments (six/treatment). The area was divided into 108 paddocks, 64 of 417m² each for the two 45 days GI treatments (16 paddocks/area replication). Others 44 paddocks of 606m² each, were allocated for the two 30 days GI treatments (11paddocks/area replication). The stocking rate was 4.5 cows/ha. The pasture was fertilized with 200kg/ha/year of N and K2O, 40kg/ha of P2O5 and 1,000kg/ha of limestone. The average fat corrected (4%) milk yields were 10.3, 10.5, 9.3 and 9.2kg/cow/day for treatments 30MF, 30BM, 45HS and 45LS, respectively. There was a significant milk yield difference (P<0.05) between the 30 and 45 day-resting periods.
Crossbred milking cows; elephantgrass; grazing interval; milk yield; rotational grazing