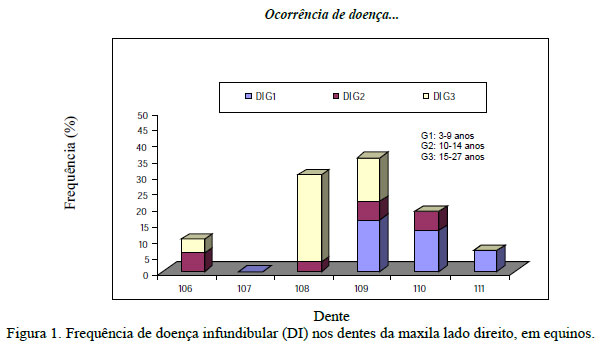
The occurrence of infundibular disease (ID) and the association between over-bite (OB) and rostral and caudal hooks on teeth of the maxilla and jaw were evaluated in 88 horses - 52 males and 36 females - aging from between 3 and 27 years old. The horses were restrained in stocks, sedated with xylazine and examined using a mouth-speculum and a stainless steel pick. The data were recorded on individual charts. The animals were grouped by age: group 1: 3 to 9, group 2: 10 to 14, and group 3: 15 to 27 years old. ID was identified on the premolar and molar teeth in 37.5% of horses. There was a positive correlation between age and number of affected teeth (r=0.26, P<0.02). The most affected teeth were the 109 (11.4%) and 209 (12.5%). The highest occurrence of ID in the most affected group (G3) was on the 108 and 208 teeth. There were 66% of OB and 65% of hooks. There was a correlation between OB and the presence of total (r=0.26, P=0.016), maxillary and mandibular (r=0.25, P=0.016), and maxillary rostral hooks (r=0.24, P=0.02). Only the association between OB and maxillary rostral hooks was significant. Animals with maxillary pre-molars hooks were 2.8 times predisposed to have OB (CI 95%=1.1 to 7.1)
horse; infundibular disease; over-bite; hook