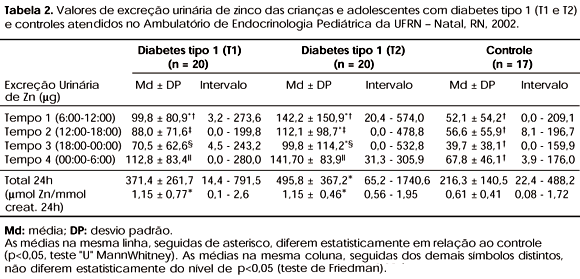
The effect of oral zinc (Zn) supplementation was investigated in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (DM1), evaluating their metabolic control and urinary Zn concentrations. Twenty DM1 patients were compared with a control group (n=17); the metabolic control included fasting glucose levels, 24h urinary glucose levels and HbA1c. Zn concentrations were measured in 24h urine before (T1) and after (T2) supplementation. DM1 patients were given oral supplements of tasteless bis-glycine chelated Zn during a 4 month period after the initial collection of baseline data. Doses were established based on the Dietary Reference Intakes. The results demonstrated unsatisfactory metabolic control due to higher HbA1c levels in some patients, after Zn supplementation. Urinary Zn excretion was higher in DM1 patients and disclosed a positive correlation with disease duration and HbA1c levels. Zn supplementation did not correct the heterogeneity of circadian variation in the studied patients, suggesting that inadequate metabolic control in DM may cause disturbances in Zn metabolism, regardless of the dietary or supplemental source.
Zinc; Supplementation; Diabetes; Urinary zinc excretion