ABSTRACT
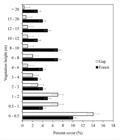
Natural communities are dynamic systems in time and space. The spatial distribution of plants and animals tends to coincide with the availability of resources needed for the survival and reproduction of each species. Natural treefall gaps offer a number of resources that influence the distribution of birds within the forest. We compared the understory bird assemblages of natural treefall gaps (15 sampling points) with those found in the adjacent forest (15 points) in the Humaitá Forest Reserve in southwestern Brazilian Amazonia. We used mist-nets to sample birds and obtained 700 captures of 105 species. Species richness, number of individuals, and species composition were all similar between gaps and forest, although six species presented some degree of association with the gaps, and nine with the forest. Nectarivores preferred gaps significantly over forest, whereas insectivores and frugivores were distributed equally between gaps and forest. Vegetation height and density differed between gaps and forest, and influenced the distribution of bird species in the two environments. Fruit availability was positively correlated with frugivore abundance in gaps. Overall, 33.3% of the birds associated with the treefall gaps are from lower forest canopy, while the others are understory species. We showed that the use of natural gaps by birds in a fragmented landscape of the Amazon forest contributes to the environmental heterogeneity and succession dynamics following natural events of habitat disturbance.
KEYWORDS:
tropical forests; Amazon region; forest fragment; understory

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail




